Page 61 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 61
2/42 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
20 -
% Speed-
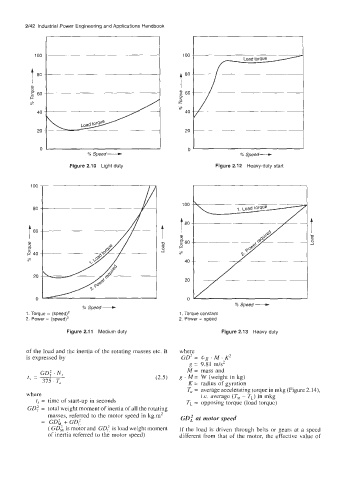
Figure 2.10 Light duty
100
100
80
t t 8o
3
P 60
e
2
P ae
e 40
ae 40
2c
20
/ % Speed -
C 0
% Speed-
1. Torque = (speed)' 1, Torque constant
2. Power w (~peed)~ 2. Power speed
Figure 2.1 1 Medium duty Figure 2.13 Heavy duty
of the load and the inertia of the rotating masses etc. It where
=
is expressed by GD~ 4.g . M . K~
g = 9.81 m/s2
M = mass and
GD; . N,
t, = (2.5) ,q . M= W (weight in kg)
375 . T, K = radius of gyration
To = average accelerating torque in mkg (Figure 2.14),
where i.e. average (Tst - TL) in mkg
t, = time of start-up in seconds TL = opposing torque (load torque)
GD; = total weight moment of inertia of all the rotating
masses, referred to the motor speed in kg.m2 GD; at motor speed
= CD; + GD;
( GDL is motor and GD: is load weight moment If the load is driven through belts or gears at a speed
of inertia referred to the motor speed) different from that of the motor, the effective value of