Page 680 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 680
Circuit interruDters 19/645
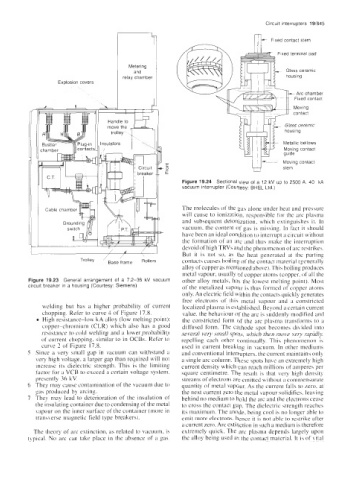
Fixed contact stem
1 Fixed terminal pad
Met!t;ng
~
Glass ceramic
relay chamber
Explosion covers
Glass ceramic
Metallic bellows
Moving contact
Moving contact
stem
~~
Figure 19.24 Sectional view of a 12 kV up to 2500 A. 40 kA
vacuum interrupter (Courtesy: BHEL Ltd.)
The molecules of the gas alone under heat and pressure
will cause to ionization. responsible for the arc plasma
and subsequent deionization, which extinguishes it. In
vacuum. the content of gas is missing. In fact it should
have been an ideal condition to interrupt a circuit without
the formation of an arc and thus make the interruption
devoid of high TRVs and the phenomenon of arc restrikes.
But it is not so, as the heat generated at the parting
contacts causes boiling of the contact material (generally
alloy of copper as mentioned above). This boiling produces
metal vapour, usually of copper atoms (copper, of all the
Figure 19.23 General arrangement of a 7.2-36 kV vacuum other alloy metals, has the lowest melting point). Most
circuit breaker in a housing (Courtesy: Siemens) of the metalized vapour is thus formed of copper atoms
only. An electric field within the contacts quickly generates
free electrons of this metal vapour and a constricted
welding but has a higher probability of current localized plasma is established. Beyond a certain current
chopping. Refer to curve 4 of Figure 17.8. value, the behaviour of the arc is suddenly modified and
High resistance-low kA alloy (low melting point): the constricted form of the arc plasma transforms to a
copper-chromium (CLR) which also has a good diffused form. The cathode spot becomes di\ided into
resistance to cold welding and a lower probability several very small spots, which then move very rapidly.
of current chopping, similar to in OCBs. Refer to repelling each other continually. This phenomenon is
curve 2 of Figure 17.8. used in current breaking in vacuum. In other mediums
5 Since a very small gap in vacuum can withstand a and conventional interrupters. the current maintains only
xry high voltage, a larger gap than required will not a single arc column. These spots have an extremely high
increase its dielectric strength. This is the limiting current density which can reach millions of amperes per
factor for a VCB to exceed a certain voltage system, square centimetre. The result is that very high density
presently 36 kV. streams of electrons are emitted without a commensurate
6 They may cause contamination of the vacuum due to quantity of metal vapour. As the current falls to zero, at
cas produced by arcing. the next current zero the metal vapour solidifies. leaving
7 They may lead to deterioration of the insulation of behind no medium to hold the arc and the electrons cease
the insulating container due to condensing ofthe metal to cross the contact gap. The dielectric strength reaches
vapour on the inner surface of the container (more in its maximum. The anode. being cool is no longer able to
trans\erse magnetic field type breakers). emit more electrons, hence it is not able to restrike after
a current zero. Arc extinction in such a medium is therefore
The theory of arc extinction, as related to vacuum, is extremely quick. The arc plasma depends largely upon
typical. No arc can take place in the absence of a gas. the alloy being used as the contact matcrial. It i$ of vital