Page 681 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 681
191646 Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
I
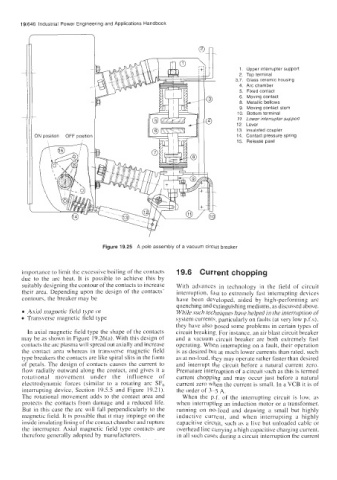
1. Upper interrupter support
2. Top terminal
3,7. Glass ceramic housing
4. Arc chamber
5. Fixed contact
6. Moving contact
8. Metallic bellows
9. Moving contact stem
10. Bottom terminal
11. Lower interrupter support
12 Lever
13. Insulated coupler
14. Contact pressure spring
15. Release pawl
Figure 19.25 A pole assembly of a vacuum circuit breaker
importance to limit the excessive boiling of the contacts 19.6 Current chopping
due to the arc heat. It is possible to achieve this by
suitably designing the contour of the contacts to increase With advances in technology in the field of circuit
their area. Depending upon the design of the contacts’ interruption, fast to extremely fast interrupting devices
contours, the breaker may be have been developed, aided by high-performing arc
quenching and extinguishing mediums, as discussed above.
Axial magnetic field type or While such techniques have helped in the interruption of
Transverse magnetic field type system currents, particularly on faults (at very low p.f.s),
they have also posed some problems in certain types of
In axial magnetic field type the shape of the contacts circuit breaking. For instance, an air blast circuit breaker
may be as shown in Figure 19.26(a). With this design of and a vacuum circuit breaker are both extremely fast
contacts the arc plasma will spread out axially and increase operating. When interrupting on a fault, their operation
the contact area whereas in transverse magnetic field is as desired but at much lower currents than rated, such
type breakers the contacts are like spiral slits in the form as at no-load, they may operate rather faster than desired
of petals. The design of contacts causes the current to and interrupt the circuit before a natural current zero.
flow radially outward along the contact, and gives it a Premature interruption of a circuit such as this is termed
rotational movement under the influence of current chopping and may occur just before a natural
electrodynamic forces (similar to a rotating arc SF, current zero when the current is small. In a VCB it is of
interrupting device, Section 19.5.5 and Figure 19.21). the order of 3-5 A.
The rotational movement adds to the contact area and When the p.f. of the interrupting circuit is low, as
protects the contacts from damage and a reduced life. when interrupting an induction motor or a transformer,
But in this case the arc will fall perpendicularly to the running on no-load and drawing a small but highly
magnetic field. It is possible that it may impinge on the inductive current, and when interrupting a highly
inside insulating lining of the contact chamber and rupture capacitive circuit, such as a live but unloaded cable or
the interrupter. Axial magnetic field type contacts are overhead line carrying a high capacitive charging current,
therefore generally adopted by manufacturers. in all such cases during a circuit interruption the current