Page 888 - Industrial Power Engineering and Applications Handbook
P. 888
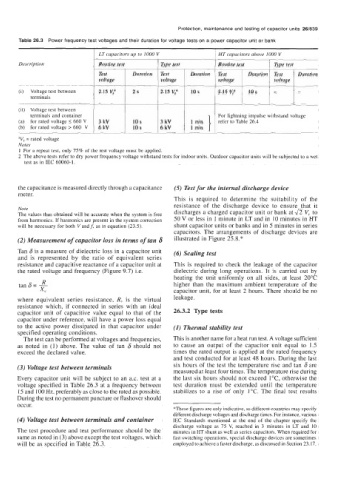
LT capacitors up to 1000 V HT capacitors above IO00 V
Description Routine test Type test Routine test Type test
Test Duration Test Duration Test Duration Test Duration
voltage voltage voltage voltage
(i) Voltage test between 2.15 V: 2s 2.15 V: 10 s 2.15 V: 10s - -
terminals
(ii) Voltage test between
terminals and container For lightning impulse withstand voltage
(a) for rated voltage 5 660 V 3 kV 10 s 3 kV refer to Table 26.4
(b) for rated voltage > 660 V 6 kV 10 s 6 kV 1 min
"V, = rated voltage
Notes
1 For a repeat test, only 75% of the test voltage must be applied.
2 The above tests refer to dry power frequency voltage withstand tests for indoor units. Outdoor capacitor units will be subjected to a wet
test as in IEC 60060- 1.
the capacitance is measured directly through a capacitbce (5) Test for the internal discharge device
meter.
This is required to determine the suitability of the
resistance of the discharge device to ensure that it
Note discharges a charged capacitor unit or bank at fi V, to
The values thus obtained will be accurate when the system is free
from harmonics. If harmonics are present in the system correction 50 V or less in 1 minute in LT and in 10 minutes in HT
will be necessary for both V andf, as in equation (23.5). shunt capacitor units or banks and in 5 minutes in series
capacitors. The arrangements of discharge devices are
(2) Measurement of capacitor loss in terms of tan 6 illustrated in Figure 25.8.*
Tan 6 is a measure of dielectric loss in a capacitor unit (6) Scaling test
and is represented by the ratio of equivalent series
resistance and capacitive reactance of a capacitor unit at This is required to check the leakage of the capacitor
the rated voltage and frequency (Figure 9.7) Le. dielectric during long operations. It is carried out by
heating the unit uniformly on all sides, at least 20°C
R
tan 6= - higher than the maximum ambient temperature of the
xc capacitor unit, for at least 2 hours. There should be no
where equivalent series resistance, R, is the virtual leakage.
resistance which, if connected in series with an ideal
capacitor unit of capacitive value equal to that of the 26.3.2 Type tests
capacitor under reference, will have a power loss equal
to the active power dissipated in that capacitor under (I) Thermal stability test
specified operating conditions.
The test can be performed at voltages and frequencies, This is another name for a heat run test. A voltage sufficient
as noted in (1) above. The value of tan 6 should not to cause an output of the capacitor unit equal to 1.5
exceed the declared value. times the rated output is applied at the rated frequency
and test conducted for at least 48 hours. During the last
(3) Voltage test between terminals six hours of the test the temperature rise and tan 6 are
measured at least four times. The temperature rise during
Every capacitor unit will be subject to an a.c. test at a the last six hours should not exceed 1"C, otherwise the
voltage specified in Table 26.3 at a frequency between test duration must be extended until the temperature
15 and 100 Hz, preferably as close to the rated as possible. stabilizes to a rise of only 1°C. The final test results
During the test no permanent puncture or flashover should
occur.
*These figures are only indicative, as different countries may specify
different discharge voltages and discharge times. For instance, various
(4) Voltage test between terminals and container IEC Standards mentioned at the end of the chapter specify the
discharge voltage as 75 V, reached in 3 minutes in LT and 10
The test procedure and test performance should be the minutes in HT shunt as well as series capacitors. When required for
same as noted in (3) above except the test voltages, which fast switching operations, special discharge devices are sometimes
will be as specified in Table 26.3. employed to achieve a faster discharge, as discussed in Section 23.17.