Page 192 - Innovations in Intelligent Machines
P. 192
184 R.W. Beard
150
p (m)
n
100
actual
50
estimated
0
0 5 10 15 20 25
100
p (m)
e
50
actual
estimated
0
0 5 10 15 20 25
200
χ(deg) actual
0
estimated
-200
0 5 10 15 20 25
time (sec)
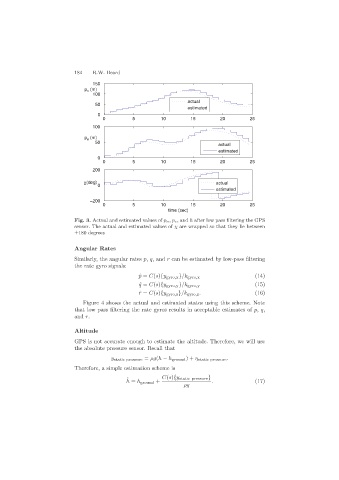
Fig. 3. Actual and estimated values of p n, p e,and h after low pass filtering the GPS
sensor. The actual and estimated values of χ are wrapped so that they lie between
±180 degrees
Angular Rates
Similarly, the angular rates p, q,and r can be estimated by low-pass filtering
the rate gyro signals:
ˆ p = C(s){y gyro,x }/k gyro,x (14)
ˆ q = C(s){y gyro,y }/k gyro,y (15)
ˆ r = C(s){y gyro,z }/k gyro,z . (16)
Figure 4 shows the actual and estimated states using this scheme. Note
that low pass filtering the rate gyros results in acceptable estimates of p, q,
and r.
Altitude
GPS is not accurate enough to estimate the altitude. Therefore, we will use
the absolute pressure sensor. Recall that
y static pressure = ρg(h − h ground )+ η static pressure .
Therefore, a simple estimation scheme is
ˆ C(s){y static pressure } . (17)
h = h ground +
ρg