Page 36 - Innovations in Intelligent Machines
P. 36
24 M.L. Cummings et al.
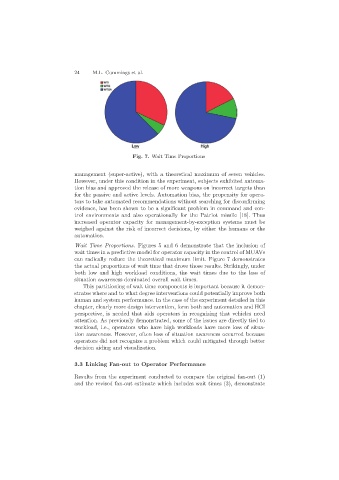
Fig. 7. Wait Time Proportions
management (super-active), with a theoretical maximum of seven vehicles.
However, under this condition in the experiment, subjects exhibited automa-
tion bias and approved the release of more weapons on incorrect targets than
for the passive and active levels. Automation bias, the propensity for opera-
tors to take automated recommendations without searching for disconfirming
evidence, has been shown to be a significant problem in command and con-
trol environments and also operationally for the Patriot missile [18]. Thus
increased operator capacity for management-by-exception systems must be
weighed against the risk of incorrect decisions, by either the humans or the
automation.
Wait Time Proportions. Figures 5 and 6 demonstrate that the inclusion of
wait times in a predictive model for operator capacity in the control of MUAVs
can radically reduce the theoretical maximum limit. Figure 7 demonstrates
the actual proportions of wait time that drove those results. Strikingly, under
both low and high workload conditions, the wait times due to the loss of
situation awareness dominated overall wait times.
This partitioning of wait time components is important because it demon-
strates where and to what degree interventions could potentially improve both
human and system performance. In the case of the experiment detailed in this
chapter, clearly more design intervention, form both and automation and HCI
perspective, is needed that aids operators in recognizing that vehicles need
attention. As previously demonstrated, some of the issues are directly tied to
workload, i.e., operators who have high workloads have more loss of situa-
tion awareness. However, often loss of situation awareness occurred because
operators did not recognize a problem which could mitigated through better
decision aiding and visualization.
3.3 Linking Fan-out to Operator Performance
Results from the experiment conducted to compare the original fan-out (1)
and the revised fan-out estimate which includes wait times (3), demonstrate