Page 184 - Inorganic Mass Spectrometry - Fundamentals and Applications
P. 184
Secondary lon Mass Spectrometry 1 71
Y
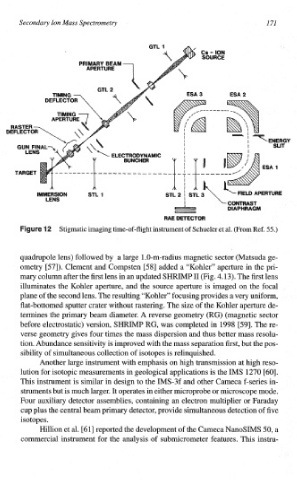
quadrupole lens) followed by a large 1.0-m-radius magnetic sector (Matsuda ge-
ometry [57]). Clement and Compsten [58] added a “Kohler” aperture in the pri-
mary column after the first lens in an updated SHRIMP I1 (Fig. 4.13). The first lens
illuminates the Kohler aperture, and the source aperture is imaged on the focal
plane of the second lens. The resulting “Kohler” focusing provides a very uniform,
at-bottomed sputter crater without rastering. The size of the Kohler aperture de-
termines the primary beam diameter. A reverse geometry (RG) (magnetic sector
before electrostatic) version, SHRIMP RG, was completed in 1998 [59]. The re-
verse geometry gives four times the mass dispersion and thus better mass resolu-
tion. Abundance sensitivity is improved with the mass separation first, but the pos-
sibility of simultaneous collection of isotopes is relinquished.
Another large instrument with emphasis on high transmission high reso-
at
lution for isotopic meas~ements in geological applications is the IMS 1270 [60].
This instrument is similar in design to the MS-3f and other Cameca f-series in-
struments but is much larger. It operates in either rnicroprobe or microscope mode,
Four auxiliary detector assemblies, containing an electron multiplier or Faraday
of
cup plus the central beam primary detector, provide simultaneous detection
five
isotopes.
Hillion et al. [61] reported the development the Cameca ~anoS1MS 50, a
of
commercial instrument for the analysis of submicrometer features. This instru-