Page 227 - Inorganic Mass Spectrometry - Fundamentals and Applications
P. 227
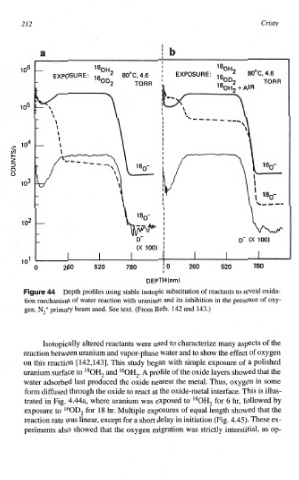
212 Cristy
2 8OoC,4.6 I EXPOSURE:
t
z)
8
l
DEPTH (nm)
ur Depth profiles using stable isotopic substitution of reactants to reveal oxida-
tion mechanis~ of water reaction with uranium and its inhibition in the presence of oxy-
gen. N,+ primary beam used. See text. (From Refs. 142 and 143.)
of
Isotopically altered reactants were used to characterize many aspects the
to
reaction between uranium and vapor-phase water and show the effect of oxygen
on this reaction [ 142,1431. This study began with simple exposure of a polished
uranium surface to l8OH2 and I60H2. A profile of the oxide layers showed that the
water adsorbed last produced the oxide nearest the metal. Thus, oxygen in some
form diffused through the oxide to react the oxide-metal interface. This is illus-
at
trated in Fig. 4.44a, where uranium was exposed to 180H2 for 6 hr, followed by
exposure to 160D2 for 18 hr. Multiple exposures of equal length showed that the
reaction rate was linear, except for a short delay in initiation (Fig. 4.45). These ex-
periments also showed that the oxygen migration was strictly interstitial, as op-