Page 88 - Inorganic Mass Spectrometry : Fundamentals and Applications
P. 88
78 Olesik
have a wide distribution of velocities. As a result, droplet-droplet collisions are
of
likely, depending on the number droplets per unit volume. Larger aerosol drops
of
may collide with the walls of the spray chamber as a result turbulence induced
losses. Drops with sufficient momentum may not be able to follow the gas flow
through the spray chamber, so these drops impact on the walls of the spray
chamber (this is called ine~tial ~e~~s~tiun). Gravitational settling is another poten-
tial means to lose large droplets as they pass through the spray chamber. Evapora-
tion results in a decrease in aerosol drop size, thereby improving the chances for
the analyte to follow the gas flow through the spray chamber and into the ICP.
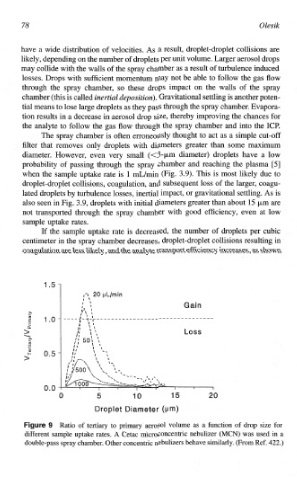
The spray chamber is often erroneously thought to act as a simple cut-off
filter that removes only droplets with diameters greater than some maximum
diameter. However, even very small (<3-pm diameter) droplets have a low
probability of passing through the spray chamber and reaching the plasma [5]
when the sample uptake rate is 1 dhin (Fig. 3.9). This is most likely due to
droplet-droplet collisions, coagulation, and subsequent loss of the larger, coagu-
As
lated droplets by turbulence losses, inertial impact, or gravitational settling. is
also seen in Fig. 3.9, droplets with initial diameters greater than about 15 pm are
not transported through the spray chamber with good efficiency, even at low
sample uptake rates.
If the sample uptake rate is decreased, the number of droplets per cubic
centimeter in the spray chamber decreases, droplet-droplet collisions resulting in
coagulation are less likely, and the analyte transport efficiency increases, as shown
,'I, 20 pL/min
l
Gain
1 .o ""-"""""
Loss
0.5
0.0
0 5 10 15 20
Droplet Diameter (vrn)
Ratio of tertiary to primary aerosol volume as a function of drop size for
different sample uptake rates. A Getac microconcentric nebulizer (MCN) was used in a
422.)
double-pass spray chamber. Other concentric nebulizers behave similarly. (From Ref.