Page 87 - Inorganic Mass Spectrometry : Fundamentals and Applications
P. 87
Inductivel~ Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry 77
mean diameter, D3,2 (a ratio of the total volume of aerosol to the total surface area).
When the nebulizer gas flow rate for a Meinhard TR-30 nebulizer was increased
from 0.6 to 1.0 L/min, the D3,2 decreased by approximately a factor of 2, from
18 to 8.7 pm [S].
The primary aerosol droplets also become slightly smaller as the sample
uptake rate is decreased. However, the Sauter mean diameter is not as sensitive to
changes in sample uptake rate as is to the nebulizer gas flow rate. For example,
it
when the uptake rate was decreased from 1.0 to 0.6 niL/min, the D3,2 value
decreased by only 4% (10.9 to 10.5 at a nebulizer gas flow rate of 0.8 L/min) [51.
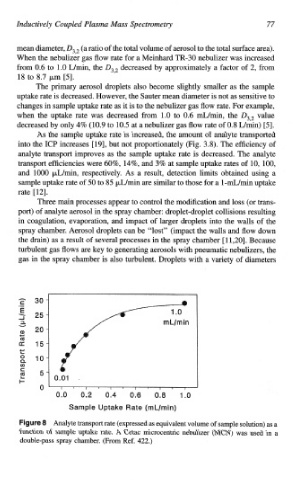
As the sample uptake rate is increased, the amount of analyte transported
into the ICP increases [ 191, but not propo~ionately (Fig. 3.8). The efficiency of
analyte transport improves as the sample uptake rate is decreased. The analyte
transport efficiencies were 60%, 14%, and 3% at sample uptake rates of 10, 100,
and 1000 p,L/min, respectively. As a result, detection limits obtained using a
sample uptake rate of 50 to 85 pL/min are similar to those for a l-niL/min uptake
rate [ 121.
Three main processes appear to control the modification and loss (or trans-
port) of analyte aerosol in the spray chamber: droplet-droplet collisions resulting
in coagulation, evaporation, and impact of larger droplets into the walls of the
spray chamber. Aerosol droplets can be "lost" (impact the walls and flow down
the drain) as a result of several processes in the spray chamber [ 1 1,201. Because
turbulent gas flows are key to generating aerosols with pneumatic nebulizers, the
gas in the spray chamber is also turbulent. Droplets with a variety of diameters
0.01 c
I ' I I l @ I I 1 1 l
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
Sample Uptake Rate (mL/min)
Figure 8 Analyte transport rate (expressed as equivalent volume sample solution) as
of
a
function of sample uptake rate. A Cetac microcentric nebulizer (MCN) was used in a
double-pass spray chamber. (From Ref. 422.)