Page 85 - Inorganic Mass Spectrometry : Fundamentals and Applications
P. 85
~nductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry 75
size was too large was not directly known until recently. At the most commonly
used rate of sample delivery to the nebulizer (1 mllmin), only 1% to 3% of the
analyte enters the plasma. The rest (97% to 99%) goes down the drain. However,
as discussed later, the analyte transport efficiency increases as the sample uptake
rate delivered to the nebulizer decreases so that similar detection limits can be
obtained at 50 p,L/min as at 1 mL,/min [12].
A spray chamber also is necessary to limit the amount of solvent that enters
the ICP (less than about 20 p,L/min of aqueous aerosol and 30 mg/min of water
is
vapor). When water aerosol and vapor loading are higher, the plasma cooled and
molecular oxide formation increases.
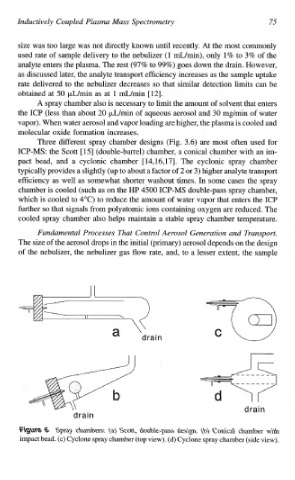
Three different spray chamber designs (Fig. 3.6) are most often used for
ICP-MS: the Scott [l51 (double-barrel) chamber, a conical chamber with an im-
pact bead, and a cyclonic chamber [ 14,16,17]. The cyclonic spray chamber
typically provides a slightly (up about a factor of 2 or 3) higher analyte transport
to
efficiency as well as somewhat shorter washout times. In some cases the spray
chamber is cooled (such as on the HP 4500 ICP-MS double-pass spray chamber,
which is cooled to 4°C) to reduce the amount of water vapor that enters the ICP
further so that signals from polyatomic ions containing oxygen are reduced. The
cooled spray chamber also helps maintain a stable spray chamber temperature.
~undamental Processes That Control Aerosol Generation and Transport.
The size of the aerosol drops in the initial (primary) aerosol depends on the design
of the nebulizer, the nebulizer gas flow rate, and, to a lesser extent, the sample
\'
drain
drain
drain
Spray chambers: (a) Scott, double-pass design. (b) Conical chamber with
impact bead. (c) Cyclone spray chamber (top view). (d) Cyclone spray chamber (side view).