Page 170 - Solutions Manual to accompany Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 170
P 23.4 kW
conv 132.6 N m
ind
m 1685 r/min 2 rad 1 min
1 r 60 s
Alternately, the induced torque can be found as
P 25.0 kW
AG 132.6 N m
ind
sync 1800 r/min 2 rad 1 min
1 r 60 s
(c) The output power of this motor is
P out P conv P mech 23,400 W 300 W 23,100 W
P 23.1 kW
load 2 rad 1 min 130.9 N m
out
m
1685 r/min 1 r 60 s
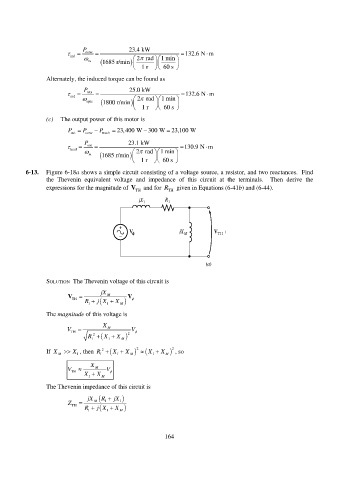
6-13. Figure 6-18a shows a simple circuit consisting of a voltage source, a resistor, and two reactances. Find
the Thevenin equivalent voltage and impedance of this circuit at the terminals. Then derive the
expressions for the magnitude of V TH and for R TH given in Equations (6-41b) and (6-44).
SOLUTION The Thevenin voltage of this circuit is
jX
V TH M V
R
1 1 X M j X
The magnitude of this voltage is
X
V TH M V
R 1 2 1 X M X 2
2
If X M X , then R 1 2 X 1 X M 2 X 1 X M , so
1
X
V M V
X X M
TH
1
The Thevenin impedance of this circuit is
jX R jX
Z TH R 1 M 1 1 X 1 M j X
164