Page 398 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 398
Further reading 381
produced being directly proportional to the mass
of moisture absorbed (Faraday's law of electro-
lysis). The response of such an instrument
obviously depends on the flow rate of gas, which
is set and controlled accurately at a predeter-
mined rate so that the current measuring meter
can be calibrated in vppm moisture. Details are
given in Chapter 19.
17.9 Further reading
Bailey, P. L., Anuljsis with Ion-selectiw Electrodes.
Heyden, London (1976)
Bates, R. G., The Determinution of pH (2nd ed.). Wiley
Interscience, New York (1973)
Durst, R. A. (ed.). Ion Selective Electrodes, National
Bureau of Standards Special Publication 314, Dept.
of Commerce, Washington, DC (1969)
Eisenman, G.. Gluss Electrodes for Hydrogen und Other
Cutions, Edward Arnold, LondonlMarcel Dekker,
New York (1967)
Freiser. H. (ed.), Ion-selective Electrodes in Anulyticul
Clwmistry, Vol. I, Plenum Press, New York (1978)
Ives, G. J. and D. J. G. Janz, Reference Electrodes,
Theory and Practice, Wiley Interscience. New York
(1961)
Midgley, D. and K. Torrance, Potentionietric Water
Analysis, Wiley Interscience. New York (1978)
Perrin, D. D. and B. Dempsey, Buflers jbr pH und
Metul Ion Control, Chapman and Hall, London
(1974)
3 Electrode lead Sawyer, D. T. and J. L. Jr Roberts, Esperiniental Elec-
trochemistry for Chemists. Wiley Interscience, New
&Airlift pump supply York (1974)
Immersion tube discharge
Liquid level
Air injection
Immersion tube
0, electrode
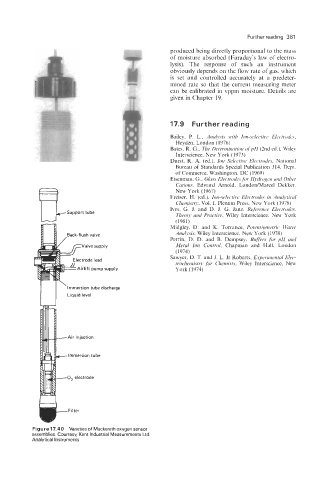
Figure 17.40 Varieties of Mackereth oxygen sensor
assemblies. Courtesy, Kent Industrial Measurements Ltd.
Analytical Instruments