Page 395 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 395
378 Chemical analysis: electrochemical techniques
cathode and anode. Oxygen will then continue to
be reduced at the cathode, causing the flow of a
current, the magnitude of which is proportional
to the partial pressure of oxygen in the sample
gas.
The only materials in contact with the process
are PVC and PTFE, and the membrane is recessed
so that it does not suffer mechanical damage. The
cell needs to be recharged with a new supply of
electrolyte at 3- or 6-month intervals depending on Yrconia tube
the operating conditions, and the membrane can
be replaced easily should it be damaged.
The cell current is amplified by a solid state
amplifier, which gives a voltage output which
can be displayed on a selection switch giving A I u m i n a
ranges of 0-1, 0-5, 0-10 or 0-25 percent oxygen tube
and a calibration adjustment. The calibration is
checked by using a reference gas, or air when the
instrument should read 20.9 percent oxygen on
the 0-25 percent scale. The instrument has an Inner
accuracy fl percent of scale range at the calibra- electrode
tion temperature but an error of f3 percent of
the reading will occur for a 16°C departure in
operating temperature.
When in use the sensor may be housed in an in-
Outer
line type housing or in a dip-type of assembly, ‘f electrode
usually made of PVC suitable for pressures up to 4 O2
gas
Measured
3.5 bar. la) Partial pressure P,
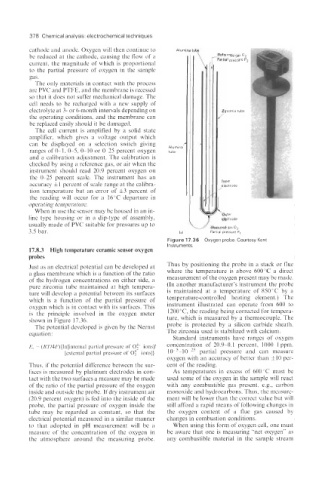
Figure 17.36 Oxygen probe. Courtesy Kent
Instruments.
17.8.3 High temperature ceramic sensor oxygen
probes
Just as an electrical potential can be developed at Thus by positioning the probe in a stack or flue
a glass membrane which is a function of the ratio where the temperature is above 600°C a direct
of the hydrogen concentrations on either side, a measurement of the oxygen present may be made.
pure zirconia tube maintained at high tempera- (In another manufacturer’s instrument the probe
ture will develop a potential between its surfaces is maintained at a temperature of 850°C by a
which is a function of the partial pressure of temperature-controlled heating element.) The
oxygen which is in contact with its surfaces. This instrument illustrated can operate from 600 to
is the principle involved in the oxygen meter 1200 “C, the reading being corrected for tempera-
shown in Figure 17.36. ture, which is measured by a thermocouple. The
The potential developed is given by the Nernst probe is protected by a silicon carbide sheath.
equation: The zirconia used is stabilized with calcium.
Standard instruments have ranges of oxygen
E, = (~~/4~){1n[internal partial pressure of 0;- ions]/ concentration of 20.9-0.1 percent, 1000-1 ppm,
[external partial pressure of 0;- ions]} 10-5-10-25 partial pressure and can measure
oxygen with an accuracy of better than +IO per-
Thus, if the potential difference between the sur- cent of the reading.
faces is measured by platinum electrodes in con- As temperatures in excess of 600°C must be
tact with the two surfaces a measure may be made used some of the oxygen in the sample will react
of the ratio of the partial pressure of the oxygen with any combustible gas present, e.g., carbon
inside and outside the probe. If dry instrument air monoxide and hydrocarbons. Thus, the measure-
(20.9 percent oxygen) is fed into the inside of the ment will be lower than the correct value but will
probe, the partial pressure of oxygen inside the still afford a rapid means of following changes in
tube may be regarded as constant, so that the the oxygen content of a flue gas caused by
electrical potential measured in a similar manner changes in combustion conditions.
to that adopted in pH measurement will be a When using this form of oxygen cell, one must
measure of the concentration of the oxygen in be aware that one is measuring “net oxygen” as
the atmosphere around the measuring probe. any combustible material in the sample stream