Page 397 - Instrumentation Reference Book 3E
P. 397
380 Chemical analysis: electrochemical techniques
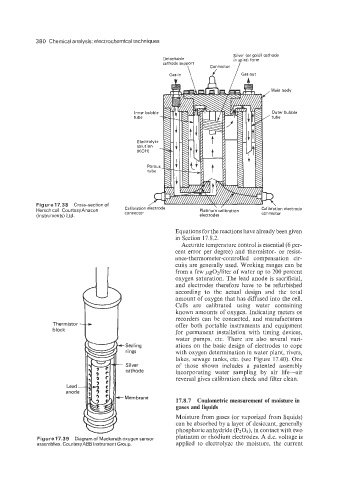
Figure 17.38 Cross-sectionof
Hersch cell. CourtesyAnacon
(Instruments) Ltd.
Equations for the reactions have already been given
in Section 17.8.2.
Accurate temperature control is essential (6 per-
cent error per degree) and thermistor- or resist-
ance-thermometer-controlled compensation cir-
cuits are generally used. Working ranges can be
from a few pgO2lliter of water up to 200 percent
oxygen saturation. The lead anode is sacrificial,
and electrodes therefore have to be refurbished
according to the actual design and the total
amount of oxygen that has diffused into the cell.
Cells are calibrated using water containing
known amounts of oxygen. Indicating meters or
recorders can be connected, and manufacturers
Thermistor - offer both portable instruments and equipment
block for permanent installation with timing devices,
water pumps, etc. There are also several vari-
Sealing ations on the basic design of electrodes to cope
rings with oxygen determination in water plant, rivers,
lakes, sewage tanks, etc. (see Figure 17.40). One
Silver of those shown includes a patented assembly
cathode incorporating water sampling by air life-air
reversal gives calibration check and filter clean.
Lead -
anode
Membrane 17.8.7 Coulometric measurement of moisture in
gases and liquids
Moisture from gases (or vaporized from liquids)
can be absorbed by a layer of desiccant, generally
phosphoric anhydride (P205), in contact with two
Figure 17.39 Diagram of Mackereth oxygen sensor platinum or rhodium electrodes. A d.c. voltage is
assemblies. CourtesyABB Instrument Group. applied to electrolyze the moisture, the current