Page 94 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 94
Machine-Train Monitoring Parameters 85
calculate belt rotational speed (rpm), the linear belt speed must first be determined by
finding the linear speed (in./min.) of the sheave at its pitch diameter. In other
words, multiply the pitch circumference (PC) by the rotational speed of the sheave,
where:
Pitch Circumference in = p ¥ Pitch Diameter in
()
()
(
(
Linear Speed in min) = Pitch Circumference in ¥ Sheave Speed rpm)
()
To find the exact rotational speed of the belt (rpm), divide the linear speed by the
length of the belt:
(
Linear Speed in min)
(
Belt Rotational Speed rpm) =
Belt Length in
()
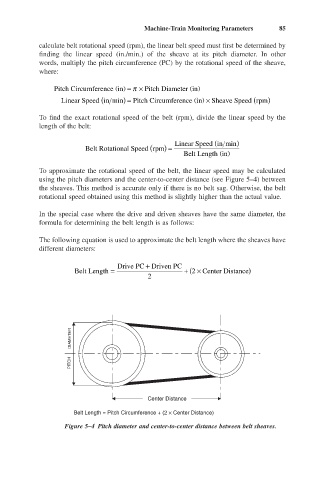
To approximate the rotational speed of the belt, the linear speed may be calculated
using the pitch diameters and the center-to-center distance (see Figure 5–4) between
the sheaves. This method is accurate only if there is no belt sag. Otherwise, the belt
rotational speed obtained using this method is slightly higher than the actual value.
In the special case where the drive and driven sheaves have the same diameter, the
formula for determining the belt length is as follows:
The following equation is used to approximate the belt length where the sheaves have
different diameters:
Drive PC Driven PC
+
Belt Length = + (2 ¥ Center Distance)
2
DIAMETER
PITCH
Center Distance
Belt Length = Pitch Circumference + (2 ¥ Center Distance)
Figure 5–4 Pitch diameter and center-to-center distance between belt sheaves.