Page 329 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 329
314 6. Interconnection with Optics
Y
R,
R,
111
A
T-. ! T,
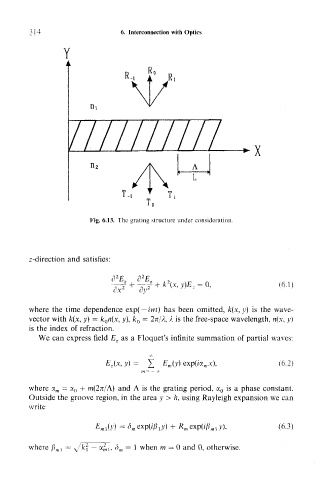
Fig. 6.13. The grating structure under consideration.
z-direction and satisfies:
,, 2
A- (x, y)E s = 0, (6.1)
where the time dependence exp( — iwt) has been omitted, k(x, y) is the wave-
vector with k(x, y) = k 0n(x, y), k 0 = 2n/A, / is the free-space wavelength, n(x y)
is the index of refraction.
We can express field E, as a Floquet's infinite summation of partial waves:
E z(x, y) exp(ia mx), (6.2)
where a m = a 0 + m(2n/A.) and A is the grating period, a 0 is a phase constant.
Outside the groove region, in the area y > h, using Rayleigh expansion we can
write
(6.3)
2
where /? m, = x/ k\ — a 1 , c5 m = 1 when m = 0 and 0, otherwise.