Page 331 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 331
316 6. Interconnection with Optics
This can be written in matrix form as follows:
E'(h) + U hE(h) = S
(6.9)
E'(0) 4- U 0E(0) = 0,
where C/ 0, U h are diagonal known matrices whose diagonal elements are:
and S is a column matrix which in fact reduces to a number [5] m =
-2ijffexp(-j0/z). m = 0.
Solution
In the case when rectangular profile Fourier coefficients in Eq. (6.5) are
constants:
C..O)-<*,-*,) exp — 2?t zm (6.10)
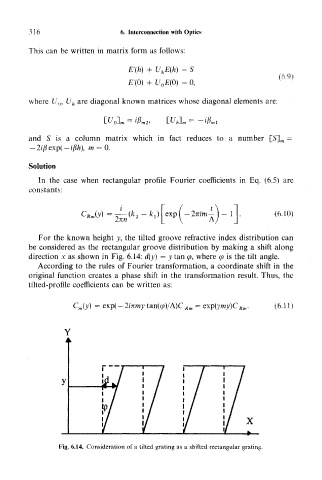
For the known height y, the tilted groove refractive index distribution can
be considered as the rectangular groove distribution by making a shift along
direction x as shown in Fig. 6.14: d(y) = y tan <p, where cp is the tilt angle.
According to the rules of Fourier transformation, a coordinate shift in the
original function creates a phase shift in the transformation result. Thus, the
tilted-profile coefficients can be written as:
,00 = exp(-2mm>> tan(<jo)/A)C Rm = Qxp(ymy)C Rm. (6.11)
Y
Fig. 6.14. Consideration of a tilted grating as a shifted rectangular grating.