Page 522 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 522
9.4. Parallel Signed-Digit Arithmetic
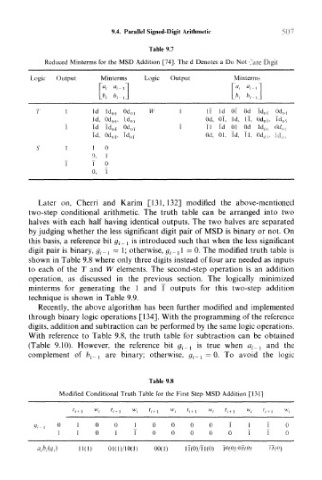
Table 9.7
Reduced Minterms for the MSD Addition [74]. The d Denotes a Do Not Care Digit
Logic Output Minterms Logic Output Minterms
T I Id Id 0] Od n, W i 11 Id Ol Od Id ol Od of
Id, Od 01, Id 01 Od, 01, Id, 11, Od oT , ld ()T
1 Id ld ()T Od oT 1 11 Id 01 Od Id 0] Od (M
Od, 01, Id, 11, Od (H . !d 0 .
Id, Od oT, ld ()T
Later on, Cherri and Karim [131,132] modified the above-mentioned
two-step conditional arithmetic. The truth table can be arranged into two
halves with each half having identical outputs. The two halves are separated
by judging whether the less significant digit pair of MSD is binary or not. On
this basis, a reference bit g £-_ l is introduced such that when the less significant
digit pair is binary, g i_ 1 = 1; otherwise, g^^l = 0. The modified truth table is
shown in Table 9.8 where only three digits instead of four are needed as inputs
to each of the T and W elements. The second-step operation is an addition
operation, as discussed in the previous section. The logically minimized
minterms for generating the 1 and 1 outputs for this two-step addition
technique is shown in Table 9.9.
Recently, the above algorithm has been further modified and implemented
through binary logic operations [134]. With the programming of the reference
digits, addition and subtraction can be performed by the same logic operations.
With reference to Table 9.8, the truth table for subtraction can be obtained
(Table 9.10). However, the reference bit #,•_., is true when a {_^ and the
complement of b^i are binary; otherwise, g i_ l=Q. To avoid the logic
Table 9.8
Modified Conditional Truth Table for the First Step MSD Addition [131]
0;-i 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0
1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
1(1) 01(0/10(1) 00(1) 11(0),/11(0) 10(0)/01(0) 11(0)