Page 526 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 526
9.4. Parallel Signed-Digit Arithmetic 51 1
binary logic operations:
1 l ! l 1
''" . *" '"' " " ' '" ' (9.35)
where © indicates the Exclusive-OR logic operation. In reality, this scheme
requires more than two steps.
9.4.2.1.3. Receded Two-Step MSD Addition/Subtraction
Another important approach for two-step addition is based on the receding
of the MSD numbers (RMSD), which was proposed by Parhami [137] and
introduced to optical computing by Awwal [138] in 1992. If there are no two
consecutive Is or Is in an MSD number, then it is possible to perform
carry-propagation-free addition. Accordingly, by exploiting the redundancy of
the MSD number system, we can derive a truth table for receding the input
binary or MSD number to achieve limited carry-free addition (see column u t
of Table 9.12). The receding algorithm converts a given MSD number X into
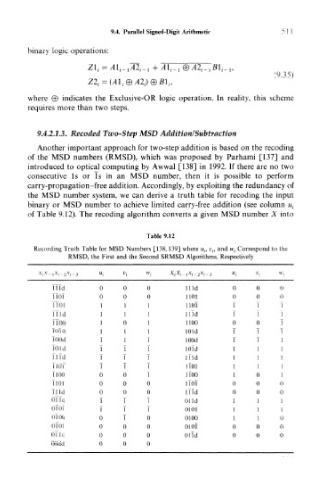
Table 9.12
Recording Truth Table for MSD Numbers [138,139] where « ;, v t, and w. Correspond to the
RMSD, the First and the Second SRMSD Algorithms, Respectively
X IX.,X J_ 2.X I_ 3 «, Vj w i **-*-*-* u i V; W;
ITTd 0 0 0 Hid 0 0 0
TToT 0 0 0 1105 0 0 0
TToi 1 1 1 1 10T T 1 I
IT id 1 1 1 IlTd T T T
TlOO 1 0 1 1100 0 0 T
Told 1 1 1 lOld T T T
fOOd T 1 I lOOd I I 1
To id T T I lOTd i 1 !
TlTd T T I Hid i 1 1
TlOf T T T U01 i 1 1
TlOO 0 0 I iTOO i 0 1
TlOi 0 0 0 HOT 0 0 0
11 Id 0 0 0 Hid 0 0 0
OTTd T I T Olid 1 1 1
oToT T T T 0101 1 i I
0100 0 T 0 0100 1 i 0
0101 0 0 0 010T 0 0 0
Olid 0 0 0 Olid 0 0 0
OOdd 0 0 0