Page 625 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 625
10.3. Distributed Fiber-Optic Sensors
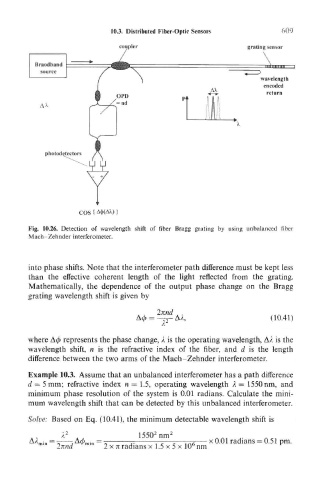
coupler grating sensor
wavelength
encoded
return
Pt
COS { A<f>(AX)}
Fig. 10.26. Detection of wavelength shift of fiber Bragg grating by using unbalanced fiber
Mach- Zehnder interferometer.
into phase shifts. Note that the interferometer path difference must be kept less
than the effective coherent length of the light reflected from the grating.
Mathematically, the dependence of the output phase change on the Bragg
grating wavelength shift is given by
2nnd
(10.41)
where A</> represents the phase change, A is the operating wavelength, A/I is the
wavelength shift, n is the refractive index of the fiber, and d is the length
difference between the two arms of the Mach-Zehnder interferometer.
Example 10.3. Assume that an unbalanced interferometer has a path difference
d = 5mm; refractive index n = 1.5, operating wavelength A — 1550 nm, and
minimum phase resolution of the system is 0.01 radians. Calculate the mini-
mum wavelength shift that can be detected by this unbalanced interferometer.
Solve: Based on Eq. (10.41), the minimum detectable wavelength shift is
x 0.01 radians = 0.51 pm.
6
2x 7i radians x 1.5 x 5 x 10 nm