Page 699 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 699
12.2. Optical Network Elements 683
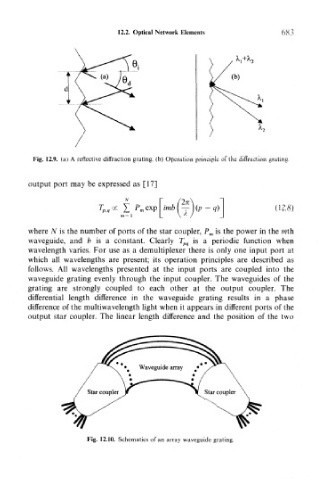
Fig. 12.9. (a) A reflective diffraction grating, (b) Operation principle of the diffraction grating.
output port may be expressed as [17]
271
imb (p - q) (12.8)
where N is the number of ports of the star coupler, P m is the power in the mth
waveguide, and b is a constant. Clearly T pq is a periodic function when
wavelength varies. For use as a demultiplexer there is only one input port at
which all wavelengths are present; its operation principles are described as
follows. All wavelengths presented at the input ports are coupled into the
waveguide grating evenly through the input coupler. The waveguides of the
grating are strongly coupled to each other at the output coupler. The
differential length difference in the waveguide grating results in a phase
difference of the multiwavelength light when it appears in different ports of the
output star coupler. The linear length difference and the position of the two
Fig. 12.10. Schematics of an array waveguide grating.