Page 394 - Introduction to Microcontrollers Architecture, Programming, and Interfacing of The Motorola 68HC12
P. 394
12,6 The M-CORE Series 371
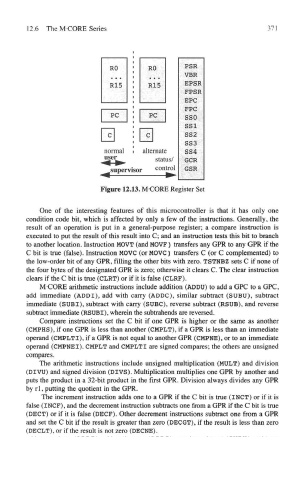
Figure 12.13. M-CORE Register Set
One of the interesting features of this microcontroller is that it has only one
condition code bit, which is affected by only a few of the instructions. Generally, the
result of an operation is put in a general-purpose register; a compare instruction is
executed to put the result of this result into C; and an instruction tests this bit to branch
to another location. Instruction MOVT (and MOVF) transfers any GPR to any GPR if the
C bit is true (false). Instruction MOVC (or MOVC ) transfers C (or C complemented) to
the low-order bit of any GPR, filling the other bits with zero. TSTNBZ sets C if none of
the four bytes of the designated GPR is zero; otherwise it clears C. The clear instruction
clears if the C bit is true (CLRT) or if it is false (CLRF).
M-CORE arithmetic instructions include addition (ADDU) to add a GPC to a GPC,
add immediate (ADDI), add with carry (ADDC), similar subtract (SUBU), subtract
immediate (SUBI), subtract with carry (SUBC), reverse subtract (RSUB), and reverse
subtract immediate (RSUBI), wherein the subtrahends are reversed.
Compare instructions set the C bit if one GPR is higher or the same as another
(CMPHS), if one GPR is less than another (CMPLT), if a GPR is less than an immediate
operand (CMPLTI), if a GPR is not equal to another GPR (CMPNE), or to an immediate
operand (CMPNEI). CMPLT and CMPLTI are signed compares; the others are unsigned
compares.
The arithmetic instructions include unsigned multiplication (MULT) and division
(DIVU) and signed division (DIVS). Multiplication multiplies one GPR by another and
puts the product in a 32-bit product in the first GPR. Division always divides any GPR
by rl, putting the quotient in the GPR.
The increment instruction adds one to a GPR if the C bit is true (INCT) or if it is
false (INCF), and the decrement instruction subtracts one from a GPR if the C bit is true
(DECT) or if it is false (DECF). Other decrement instructions subtract one from a GPR
and set the C bit if the result is greater than zero (DECGT), if the result is less than zero
(DECLT), or if the result is not zero (DECNE).