Page 153 - Introduction to Mineral Exploration
P. 153
136 J. MILSOM
uranium in the potassium window. It is usual
Counts to also record total count but discrimination is
important, as was shown by the discovery of
the Yeeleerie uranium deposit in Western Aus-
10,000
tralia in a salt lake where the radiometric
anomaly had initially been attributed to potash
in the evaporites. Interpretational difficulties
are introduced in the search for uranium by the
1000 fact that 214 Bi lies below radon in the decay
chain. Radon is a gas and the isotope concerned
has a half-life of several days, allowing con-
Potassium siderable dispersion from the primary source.
(1.46 MeV)
100 The unpopularity of nuclear power, and the
availability of uranium from dismantled nu-
clear bombs, made exploration for uranium
Uranium
(1.76 MeV) much less attractive, and the importance of
Thorium radiometric methods declined accordingly.
10 (2.615 MeV) Much of the radiometric work being under-
taken at present is for public health purposes
and in such applications the monitoring of
alpha particles from radon gas using alpha cups
and alpha cards may be as useful as the detec-
1.0 2.0 tion of gamma rays. Gamma-ray surveys do,
however, have geological applications in locat-
Energy (MeV)
ing alteration zones in acid and intermediate
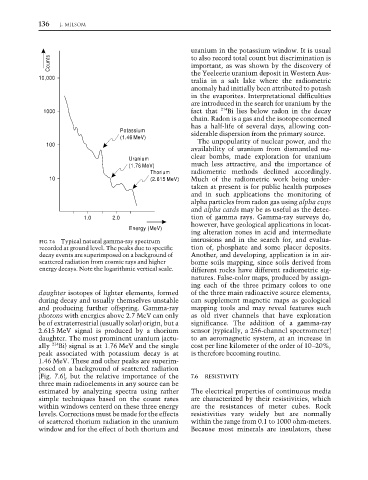
FIG. 7.6 Typical natural gamma-ray spectrum intrusions and in the search for, and evalua-
recorded at ground level. The peaks due to specific tion of, phosphate and some placer deposits.
decay events are superimposed on a background of Another, and developing, application is in air-
scattered radiation from cosmic rays and higher borne soils mapping, since soils derived from
energy decays. Note the logarithmic vertical scale. different rocks have different radiometric sig-
natures. False-color maps, produced by assign-
ing each of the three primary colors to one
daughter isotopes of lighter elements, formed of the three main radioactive source elements,
during decay and usually themselves unstable can supplement magnetic maps as geological
and producing further offspring. Gamma-ray mapping tools and may reveal features such
photons with energies above 2.7 MeV can only as old river channels that have exploration
be of extraterrestrial (usually solar) origin, but a significance. The addition of a gamma-ray
2.615 MeV signal is produced by a thorium sensor (typically, a 256-channel spectrometer)
daughter. The most prominent uranium (actu- to an aeromagnetic system, at an increase in
ally 214 Bi) signal is at 1.76 MeV and the single cost per line kilometer of the order of 10–20%,
peak associated with potassium decay is at is therefore becoming routine.
1.46 MeV. These and other peaks are superim-
posed on a background of scattered radiation
(Fig. 7.6), but the relative importance of the 7.6 RESISTIVITY
three main radioelements in any source can be
estimated by analyzing spectra using rather The electrical properties of continuous media
simple techniques based on the count rates are characterized by their resistivities, which
within windows centerd on these three energy are the resistances of meter cubes. Rock
levels. Corrections must be made for the effects resistivities vary widely but are normally
of scattered thorium radiation in the uranium within the range from 0.1 to 1000 ohm-meters.
window and for the effect of both thorium and Because most minerals are insulators, these