Page 98 - Introduction to Mineral Exploration
P. 98
5: FROM PROSPECT TO PREFEASIBILITY 81
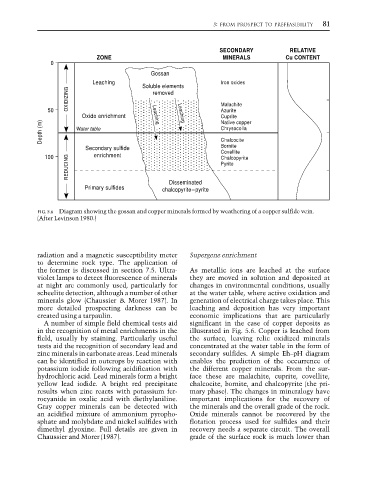
SECONDARY RELATIVE
ZONE MINERALS Cu CONTENT
0
Gossan
Leaching Soluble elements Iron oxides
OXIDIZING removed Malachite
50 Leaching Azurite
Oxide enrichment Leaching Cuprite
Depth (m) Water table Chrysocolla
Native copper
Chalcocite
Secondary sulfide Bornite
Covellite
REDUCING Pyrite
100 enrichment Chalcopyrite
Disseminated
Primary sulfides chalcopyrite–pyrite
FIG. 5.6 Diagram showing the gossan and copper minerals formed by weathering of a copper sulfide vein.
(After Levinson 1980.)
radiation and a magnetic susceptibility meter Supergene enrichment
to determine rock type. The application of
the former is discussed in section 7.5. Ultra- As metallic ions are leached at the surface
violet lamps to detect fluorescence of minerals they are moved in solution and deposited at
at night are commonly used, particularly for changes in environmental conditions, usually
scheelite detection, although a number of other at the water table, where active oxidation and
minerals glow (Chaussier & Morer 1987). In generation of electrical charge takes place. This
more detailed prospecting darkness can be leaching and deposition has very important
created using a tarpaulin. economic implications that are particularly
A number of simple field chemical tests aid significant in the case of copper deposits as
in the recognition of metal enrichments in the illustrated in Fig. 5.6. Copper is leached from
field, usually by staining. Particularly useful the surface, leaving relic oxidized minerals
tests aid the recognition of secondary lead and concentrated at the water table in the form of
zinc minerals in carbonate areas. Lead minerals secondary sulfides. A simple Eh–pH diagram
can be identified in outcrops by reaction with enables the prediction of the occurrence of
potassium iodide following acidification with the different copper minerals. From the sur-
hydrochloric acid. Lead minerals form a bright face these are malachite, cuprite, covellite,
yellow lead iodide. A bright red precipitate chalcocite, bornite, and chalcopyrite (the pri-
results when zinc reacts with potassium fer- mary phase). The changes in mineralogy have
rocyanide in oxalic acid with diethylaniline. important implications for the recovery of
Gray copper minerals can be detected with the minerals and the overall grade of the rock.
an acidified mixture of ammonium pyropho- Oxide minerals cannot be recovered by the
sphate and molybdate and nickel sulfides with flotation process used for sulfides and their
dimethyl glyoxine. Full details are given in recovery needs a separate circuit. The overall
Chaussier and Morer (1987). grade of the surface rock is much lower than