Page 291 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 291
PERFORMANCE OF CONVENTIONAL OIL AND GAS RESERVOIRS 279
Beaufort Prudhoe Bay
Sea
Russia
Trans Alaska
Pipeline
Canada
Alaska
Anchorage
Bering Valdez
Sea
Pacific
Ocean
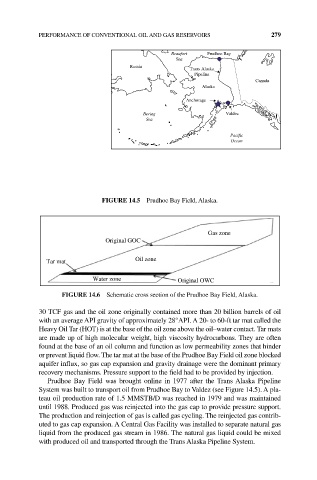
FIgURE 14.5 Prudhoe Bay Field, Alaska.
Gas zone
Original GOC
Tar mat Oil zone
Water zone Original OWC
FIgURE 14.6 Schematic cross section of the Prudhoe Bay Field, Alaska.
30 TCF gas and the oil zone originally contained more than 20 billion barrels of oil
with an average API gravity of approximately 28°API. A 20‐ to 60‐ft tar mat called the
Heavy Oil Tar (HOT) is at the base of the oil zone above the oil–water contact. Tar mats
are made up of high molecular weight, high viscosity hydrocarbons. They are often
found at the base of an oil column and function as low permeability zones that hinder
or prevent liquid flow. The tar mat at the base of the Prudhoe Bay Field oil zone blocked
aquifer influx, so gas cap expansion and gravity drainage were the dominant primary
recovery mechanisms. Pressure support to the field had to be provided by injection.
Prudhoe Bay Field was brought online in 1977 after the Trans Alaska Pipeline
System was built to transport oil from Prudhoe Bay to Valdez (see Figure 14.5). A pla‑
teau oil production rate of 1.5 MMSTB/D was reached in 1979 and was maintained
until 1988. Produced gas was reinjected into the gas cap to provide pressure support.
The production and reinjection of gas is called gas cycling. The reinjected gas contrib‑
uted to gas cap expansion. A Central Gas Facility was installed to separate natural gas
liquid from the produced gas stream in 1986. The natural gas liquid could be mixed
with produced oil and transported through the Trans Alaska Pipeline System.