Page 112 - Introduction to Transfer Phenomena in PEM Fuel Cells
P. 112
Mass Transfer Phenomena 101
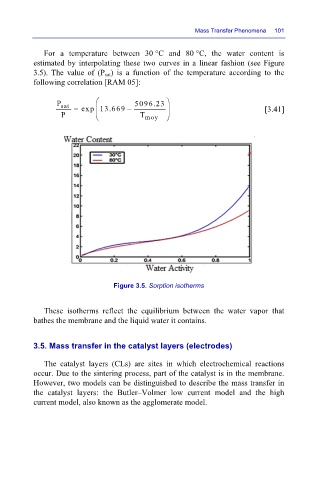
For a temperature between 30 °C and 80 °C, the water content is
estimated by interpolating these two curves in a linear fashion (see Figure
3.5). The value of (P sat) is a function of the temperature according to the
following correlation [RAM 05]:
P sat = exp 13.669 − 5096.23
P T moy [3.41]
Figure 3.5. Sorption isotherms
These isotherms reflect the equilibrium between the water vapor that
bathes the membrane and the liquid water it contains.
3.5. Mass transfer in the catalyst layers (electrodes)
The catalyst layers (CLs) are sites in which electrochemical reactions
occur. Due to the sintering process, part of the catalyst is in the membrane.
However, two models can be distinguished to describe the mass transfer in
the catalyst layers: the Butler–Volmer low current model and the high
current model, also known as the agglomerate model.