Page 157 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 157
136 Introduction to Microfabrication
removing different types of contamination. Table 12.1 Table 12.2 Sources of particles
lists the main wet-cleaning solutions commonly in
– Chemical reactions in deposition and etching
use. Cleaning is always closely connected with both
– Moving parts in tools: robot arms, valves, doors
preceding and following process steps, and therefore
– Static parts: wafer holders, cassettes, o-rings
cleaning strategies in different labs and wafer fabs can
– Vacuum: pumping, venting, condensation
be very different in respect to cleaning bath chemistry,
– Gases, chemicals, water
bath sequence, concentration, time and temperature. For
instance, instead of the standard ammonia peroxide
clean in 1:1:5 NH 4 OH:H 2 O 2 :H 2 O ratios, some users
contaminant, but lithography- and topography-forming
prefer 1:4:100, and even though all users do employ
steps will be aware of it.
the ammonia peroxide step in pre-oxidation cleaning,
Fabrication processes themselves are major sources
additional HCl:H 2 O 2 , HF and H 2 SO 4 :H 2 O 2 cleans are
of particles. Listed in Table 12.2 are some materials and
combined in variegated ways.
mechanisms that contribute to particle contamination.
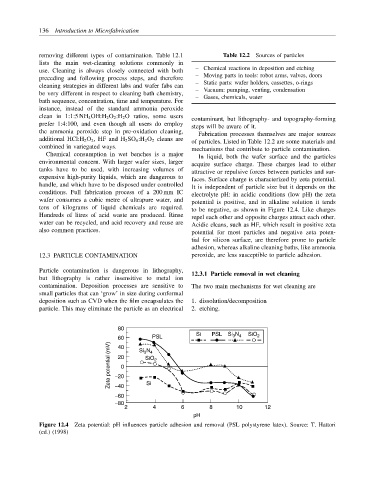
Chemical consumption in wet benches is a major In liquid, both the wafer surface and the particles
environmental concern. With larger wafer sizes, larger acquire surface charge. These charges lead to either
tanks have to be used, with increasing volumes of attractive or repulsive forces between particles and sur-
expensive high-purity liquids, which are dangerous to faces. Surface charge is characterized by zeta potential.
handle, and which have to be disposed under controlled It is independent of particle size but it depends on the
conditions. Full fabrication process of a 200 mm IC electrolyte pH: in acidic conditions (low pH) the zeta
wafer consumes a cubic metre of ultrapure water, and potential is positive, and in alkaline solution it tends
tens of kilograms of liquid chemicals are required. to be negative, as shown in Figure 12.4. Like charges
Hundreds of litres of acid waste are produced. Rinse repel each other and opposite charges attract each other.
water can be recycled, and acid recovery and reuse are Acidic cleans, such as HF, which result in positive zeta
also common practices. potential for most particles and negative zeta poten-
tial for silicon surface, are therefore prone to particle
adhesion, whereas alkaline cleaning baths, like ammonia
12.3 PARTICLE CONTAMINATION peroxide, are less susceptible to particle adhesion.
Particle contamination is dangerous in lithography,
12.3.1 Particle removal in wet cleaning
but lithography is rather insensitive to metal ion
contamination. Deposition processes are sensitive to The two main mechanisms for wet cleaning are
small particles that can ‘grow’ in size during conformal
deposition such as CVD when the film encapsulates the 1. dissolution/decomposition
particle. This may eliminate the particle as an electrical 2. etching.
80
3 4
60 Si N PSL Si PSL Si N SiO 2
Zeta potential (mV) −20 0 3 4 2
40
20
SiO
−40
−60 Si
−80
2 4 6 8 10 12
pH
Figure 12.4 Zeta potential: pH influences particle adhesion and removal (PSL polystyrene latex). Source: T. Hattori
(ed.) (1998)