Page 152 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 152
Etching 131
4. How much underlying oxide is lost when a tungsten
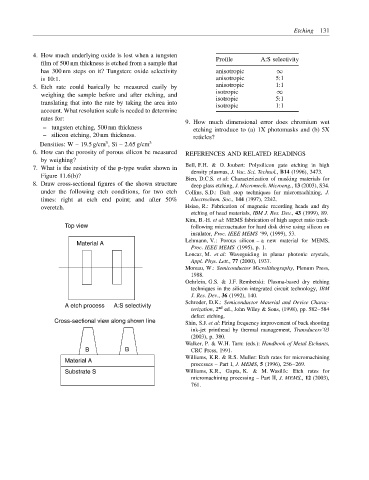
Profile A:S selectivity
film of 500 nm thickness is etched from a sample that
has 300 nm steps on it? Tungsten: oxide selectivity anisotropic ∞
is 10:1. anisotropic 5:1
5. Etch rate could basically be measured easily by anisotropic 1:1
isotropic ∞
weighing the sample before and after etching, and
isotropic 5:1
translating that into the rate by taking the area into
isotropic 1:1
account. What resolution scale is needed to determine
rates for:
9. How much dimensional error does chromium wet
– tungsten etching, 500 nm thickness etching introduce to (a) 1X photomasks and (b) 5X
– silicon etching, 20 nm thickness. reticles?
3
Densities: W – 19.5 g/cm , Si – 2.65 g/cm 3
6. How can the porosity of porous silicon be measured REFERENCES AND RELATED READINGS
by weighing?
Bell, F.H. & O. Joubert: Polysilicon gate etching in high
7. What is the resistivity of the p-type wafer shown in density plasmas, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., B14 (1996), 3473.
Figure 11.6(b)?
Bien, D.C.S. et al: Characterization of masking materials for
8. Draw cross-sectional figures of the shown structure deep glass etching, J. Micromech. Microeng., 13 (2003), S34.
under the following etch conditions, for two etch Collins, S.D.: Etch stop techniques for micromachining, J.
times: right at etch end point; and after 50% Electrochem. Soc., 144 (1997), 2242.
overetch. Hsiao, R.: Fabrication of magnetic recording heads and dry
etching of head materials, IBM J. Res. Dev., 43 (1999), 89.
Kim, B.-H. et al: MEMS fabrication of high aspect ratio track-
Top view following microactuator for hard disk drive using silicon on
insulator, Proc. IEEE MEMS ‘99, (1999), 53.
Material A Lehmann, V.: Porous silicon – a new material for MEMS,
Proc. IEEE MEMS (1995), p. 1.
Loncar, M. et al: Waveguiding in planar photonic crystals,
Appl. Phys. Lett., 77 (2000), 1937.
Moreau, W.: Semiconductor Microlithography, Plenum Press,
1988.
Oehrlein, G.S. & J.F. Rembetski: Plasma-based dry etching
techniques in the silicon integrated circuit technology, IBM
J. Res. Dev., 36 (1992), 140.
A etch process A:S selectivity Schroder, D.K.: Semiconductor Material and Device Charac-
terization, 2 nd ed., John Wiley & Sons, (1998), pp. 582–584
defect etching.
Cross-sectional view along shown line Shin, S.J. et al: Firing frequency improvement of back shooting
ink-jet printhead by thermal management, Transducers’03
(2003), p. 380.
Walker, P. & W.H. Tarn: (eds.): Handbook of Metal Etchants,
B B CRC Press, 1991.
Material A Williams, K.R. & R.S. Muller: Etch rates for micromachining
processes – Part I, J. MEMS, 5 (1996), 256–269.
Substrate S Williams, K.R., Gupta, K. & M. Wasilik: Etch rates for
micromachining processing – Part II, J. MEMS., 12 (2003),
761.