Page 360 - Sami Franssila Introduction to Microfabrication
P. 360
Integrated Processing 339
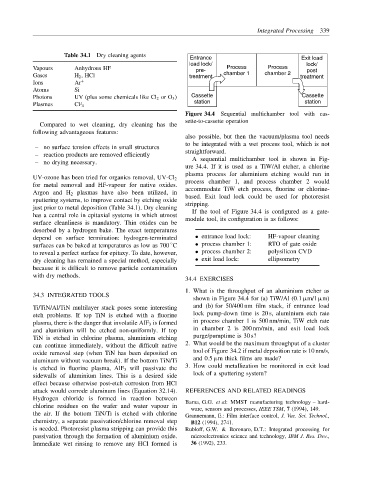
Table 34.1 Dry cleaning agents Entrance Exit load
load lock/ lock/
Vapours Anhydrous HF pre- Process Process post
Gases H 2 , HCl treatment chamber 1 chamber 2 treatment
Ions Ar +
Atoms Si
Photons UV (plus some chemicals like Cl 2 or O 3 ) Cassette Cassette
station station
Plasmas CF 4
Figure 34.4 Sequential multichamber tool with cas-
sette-to-cassette operation
Compared to wet cleaning, dry cleaning has the
following advantageous features:
also possible, but then the vacuum/plasma tool needs
to be integrated with a wet process tool, which is not
– no surface tension effects in small structures
straightforward.
– reaction products are removed efficiently
A sequential multichamber tool is shown in Fig-
– no drying necessary.
ure 34.4. If it is used as a TiW/Al etcher, a chlorine
plasma process for aluminium etching would run in
UV-ozone has been tried for organics removal, UV-Cl 2 process chamber 1, and process chamber 2 would
for metal removal and HF-vapour for native oxides.
Argon and H 2 plasmas have also been utilized, in accommodate TiW etch process, fluorine or chlorine-
sputtering systems, to improve contact by etching oxide based. Exit load lock could be used for photoresist
just prior to metal deposition (Table 34.1). Dry cleaning stripping.
has a central role in epitaxial systems in which utmost If the tool of Figure 34.4 is configured as a gate-
surface cleanliness is mandatory. Thin oxides can be module tool, its configuration is as follows:
desorbed by a hydrogen bake. The exact temperatures
depend on surface termination: hydrogen-terminated • entrance load lock: HF-vapour cleaning
surfaces can be baked at temperatures as low as 700 C • process chamber 1: RTO of gate oxide
◦
to reveal a perfect surface for epitaxy. To date, however, • process chamber 2: polysilicon CVD
dry cleaning has remained a special method, especially • exit load lock: ellipsometry
because it is difficult to remove particle contamination
with dry methods.
34.4 EXERCISES
1. What is the throughput of an aluminium etcher as
34.3 INTEGRATED TOOLS
shown in Figure 34.4 for (a) TiW/Al (0.1 µm/1 µm)
Ti/TiN/Al/TiN multilayer stack poses some interesting and (b) for 50/400 nm film stack, if entrance load
etch problems. If top TiN is etched with a fluorine lock pump-down time is 20 s, aluminium etch rate
plasma, there is the danger that involatile AlF 3 is formed in process chamber 1 is 500 nm/min, TiW etch rate
and aluminium will be etched non-uniformly. If top in chamber 2 is 200 nm/min, and exit load lock
TiN is etched in chlorine plasma, aluminium etching purge/pumptime is 30 s?
can continue immediately, without the difficult native 2. What would be the maximum throughput of a cluster
oxide removal step (when TiN has been deposited on tool of Figure 34.2 if metal deposition rate is 10 nm/s,
aluminum without vacuum break). If the bottom TiN/Ti and 0.5 µm thick films are made?
is etched in fluorine plasma, AlF 3 will passivate the 3. How could metallization be monitored in exit load
sidewalls of aluminium lines. This is a desired side lock of a sputtering system?
effect because otherwise post-etch corrosion from HCl
attack would corrode aluminum lines (Equation 32.14). REFERENCES AND RELATED READINGS
Hydrogen chloride is formed in reaction between Barna, G.G. et al: MMST manufacturing technology – hard-
chlorine residues on the wafer and water vapour in ware, sensors and processes, IEEE TSM, 7 (1994), 149.
the air. If the bottom TiN/Ti is etched with chlorine Grannemann, E.: Film interface control, J. Vac. Sci. Technol.,
chemistry, a separate passivation/chlorine removal step B12 (1994), 2741.
is needed. Photoresist plasma stripping can provide this Rubloff, G.W. & Boronaro, D.T.: Integrated processing for
passivation through the formation of aluminium oxide. microelectronics science and technology, IBM J. Res. Dev.,
Immediate wet rinsing to remove any HCl formed is 36 (1992), 233.