Page 227 -
P. 227
210 Chapter 6
Unifying user interface
Profiles for User views
personalization or representations
UI layer
Applications Functions for KM
Process
Help Locate Record Find Alert to layer
system experts BPs associations new factors
Metadata
Data
layer
Data sources Data types Data formats
Figure 6.10
KM organizational architecture
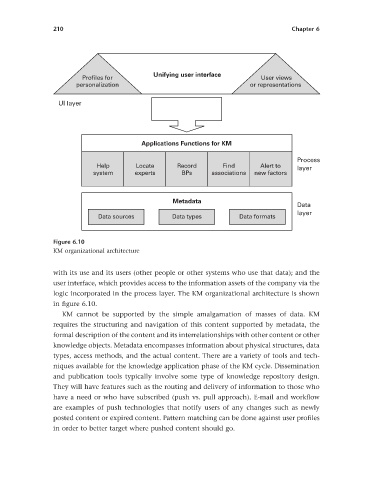
with its use and its users (other people or other systems who use that data); and the
user interface, which provides access to the information assets of the company via the
logic incorporated in the process layer. The KM organizational architecture is shown
in fi gure 6.10 .
KM cannot be supported by the simple amalgamation of masses of data. KM
requires the structuring and navigation of this content supported by metadata, the
formal description of the content and its interrelationships with other content or other
knowledge objects. Metadata encompasses information about physical structures, data
types, access methods, and the actual content. There are a variety of tools and tech-
niques available for the knowledge application phase of the KM cycle. Dissemination
and publication tools typically involve some type of knowledge repository design.
They will have features such as the routing and delivery of information to those who
have a need or who have subscribed (push vs. pull approach). E-mail and workfl ow
are examples of push technologies that notify users of any changes such as newly
posted content or expired content. Pattern matching can be done against user profi les
in order to better target where pushed content should go.