Page 332 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 332
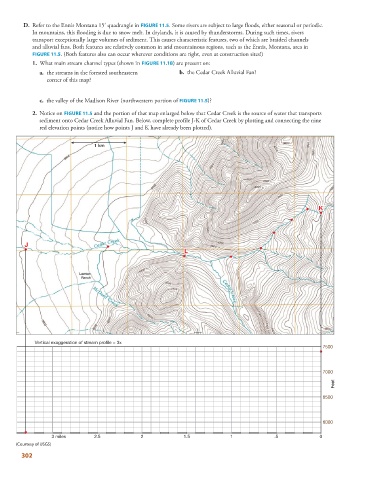
D. Refer to the Ennis Montana 15’ quadrangle in FIGURE 11.5 . Some rivers are subject to large floods, either seasonal or periodic.
In mountains, this flooding is due to snow melt. In drylands, it is caused by thunderstorms. During such times, rivers
transport exceptionally large volumes of sediment. This causes characteristic features, two of which are braided channels
and alluvial fans. Both features are relatively common in arid mountainous regions, such as the Ennis, Montana, area in
FIGURE 11.5 . (Both features also can occur wherever conditions are right, even at construction sites!)
1. What main stream channel types (shown in FIGURE 11.1B ) are present on:
a. the streams in the forested southeastern b. the Cedar Creek Alluvial Fan?
corner of this map?
c. the valley of the Madison River (northwestern portion of FIGURE 11.5 )?
2. Notice on FIGURE 11.5 and the portion of that map enlarged below that Cedar Creek is the source of water that transports
sediment onto Cedar Creek Alluvial Fan. Below, complete profile J-K of Cedar Creek by plotting and connecting the nine
red elevation points (notice how points J and K have already been plotted).
1 km
K K
J J
L L
Vertical exaggeration of stream profile = 3x
7500
7000
Feet
6500
6000
3 miles 2.5 2 1.5 1 .5 0
(Courtesy of USGS)
302