Page 343 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 343
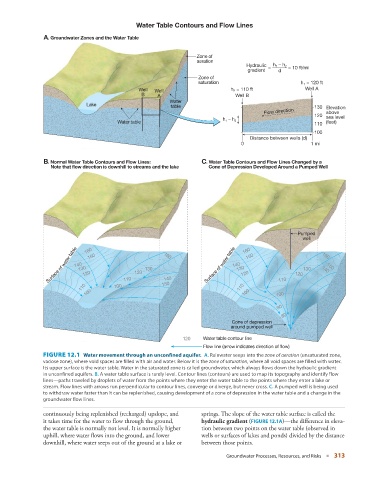
Water Table Contours and Flow Lines
A. Groundwater Zones and the Water Table
Zone of
aeration
Hydraulic = h 1 – h 2 = 10 ft/mi
gradient d
Zone of
saturation h 1 = 120 ft
Well Well h 2 = 110 ft Well A
B A Well B
Water
Lake table 130 Elevation
Flow direction above
120 sea level
Water table h 1 – h 2 110 (feet)
100
Distance between wells (d)
0 1 mi
B. Normal Water Table Contours and Flow Lines: C. Water Table Contours and Flow Lines Changed by a
Note that flow direction is downhill to streams and the lake Cone of Depression Developed Around a Pumped Well
Pumped
well
Surface of water table 140 130 120 150 120 130 160 Surface of water table 140 130 120 150 120 130 140
160
160
160
150
140
110 100 110 150 110 110
100 100 100
90
80
Cone of depression
around pumped well
120 Water table contour line
Flow line (arrow indicates direction of flow)
FIGURE 12.1 Water movement through an unconfined aquifer. A. Rainwater seeps into the zone of aeration (unsaturated zone,
vadose zone), where void spaces are filled with air and water. Below it is the zone of saturation, where all void spaces are filled with water.
Its upper surface is the water table. Water in the saturated zone is called groundwater, which always flows down the hydraulic gradient
in unconfined aquifers. B. A water table surface is rarely level. Contour lines (contours) are used to map its topography and identify flow
lines—paths traveled by droplets of water from the points where they enter the water table to the points where they enter a lake or
stream. Flow lines with arrows run perpendicular to contour lines, converge or diverge, but never cross. C. A pumped well is being used
to withdraw water faster than it can be replenished, causing development of a cone of depression in the water table and a change in the
groundwater flow lines.
continuously being replenished (recharged) upslope, and springs. The slope of the water table surface is called the
it takes time for the water to flow through the ground, hydraulic gradient ( FIGURE 12.1A )—the difference in eleva-
the water table is normally not level. It is normally higher tion between two points on the water table (observed in
uphill, where water flows into the ground, and lower wells or surfaces of lakes and ponds) divided by the distance
downhill, where water seeps out of the ground at a lake or between those points.
Groundwater Processes, Resources, and Risks ■ 313