Page 197 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 197
9.4 Case study 195
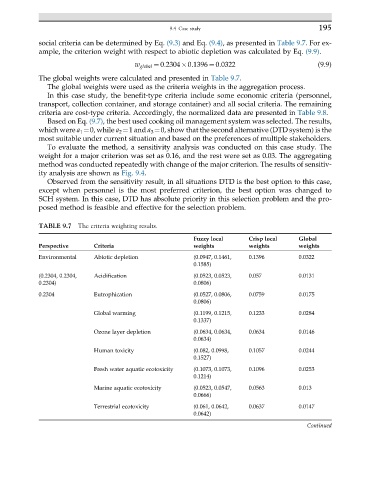
social criteria can be determined by Eq. (9.3) and Eq. (9.4), as presented in Table 9.7. For ex-
ample, the criterion weight with respect to abiotic depletion was calculated by Eq. (9.9).
w global ¼ 0:2304 0:1396 ¼ 0:0322 (9.9)
The global weights were calculated and presented in Table 9.7.
The global weights were used as the criteria weights in the aggregation process.
In this case study, the benefit-type criteria include some economic criteria (personnel,
transport, collection container, and storage container) and all social criteria. The remaining
criteria are cost-type criteria. Accordingly, the normalized data are presented in Table 9.8.
Based on Eq. (9.7), the best used cooking oil management system was selected. The results,
which were a 1 ¼0, while a 2 ¼1 and a 3 ¼0, show that the second alternative (DTD system) is the
most suitable under current situation and based on the preferences of multiple stakeholders.
To evaluate the method, a sensitivity analysis was conducted on this case study. The
weight for a major criterion was set as 0.16, and the rest were set as 0.03. The aggregating
method was conducted repeatedly with change of the major criterion. The results of sensitiv-
ity analysis are shown as Fig. 9.4.
Observed from the sensitivity result, in all situations DTD is the best option to this case,
except when personnel is the most preferred criterion, the best option was changed to
SCH system. In this case, DTD has absolute priority in this selection problem and the pro-
posed method is feasible and effective for the selection problem.
TABLE 9.7 The criteria weighting results.
Fuzzy local Crisp local Global
Perspective Criteria weights weights weights
Environmental Abiotic depletion (0.0947, 0.1461, 0.1396 0.0322
0.1585)
(0.2304, 0.2304, Acidification (0.0523, 0.0523, 0.057 0.0131
0.2304) 0.0806)
0.2304 Eutrophication (0.0527, 0.0806, 0.0759 0.0175
0.0806)
Global warming (0.1199, 0.1215, 0.1233 0.0284
0.1337)
Ozone layer depletion (0.0634, 0.0634, 0.0634 0.0146
0.0634)
Human toxicity (0.082, 0.0998, 0.1057 0.0244
0.1527)
Fresh water aquatic ecotoxicity (0.1073, 0.1073, 0.1096 0.0253
0.1214)
Marine aquatic ecotoxicity (0.0523, 0.0547, 0.0563 0.013
0.0666)
Terrestrial ecotoxicity (0.061, 0.0642, 0.0637 0.0147
0.0642)
Continued