Page 110 - Low Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
P. 110
Effective use of heat pumps for various heating applications 99
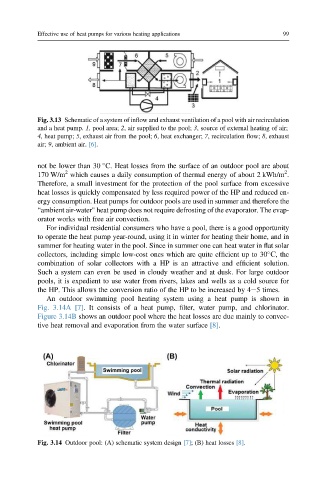
Fig. 3.13 Schematic of a system of inflow and exhaust ventilation of a pool with air recirculation
and a heat pump. 1, pool area; 2, air supplied to the pool; 3, source of external heating of air;
4, heat pump; 5, exhaust air from the pool; 6, heat exchanger; 7, recirculation flow; 8, exhaust
air; 9, ambient air. [6].
not be lower than 30 C. Heat losses from the surface of an outdoor pool are about
2
2
170 W/m which causes a daily consumption of thermal energy of about 2 kWh/m .
Therefore, a small investment for the protection of the pool surface from excessive
heat losses is quickly compensated by less required power of the HP and reduced en-
ergy consumption. Heat pumps for outdoor pools are used in summer and therefore the
“ambient air-water" heat pump does not require defrosting of the evaporator. The evap-
orator works with free air convection.
For individual residential consumers who have a pool, there is a good opportunity
to operate the heat pump year-round, using it in winter for heating their home, and in
summer for heating water in the pool. Since in summer one can heat water in flat solar
collectors, including simple low-cost ones which are quite efficient up to 30 S, the
combination of solar collectors with a HP is an attractive and efficient solution.
Such a system can even be used in cloudy weather and at dusk. For large outdoor
pools, it is expedient to use water from rivers, lakes and wells as a cold source for
the HP. This allows the conversion ratio of the HP to be increased by 4e5 times.
An outdoor swimming pool heating system using a heat pump is shown in
Fig. 3.14A [7]. It consists of a heat pump, filter, water pump, and chlorinator.
Figure 3.14B shows an outdoor pool where the heat losses are due mainly to convec-
tive heat removal and evaporation from the water surface [8].
Fig. 3.14 Outdoor pool: (A) schematic system design [7]; (B) heat losses [8].