Page 106 - Low Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
P. 106
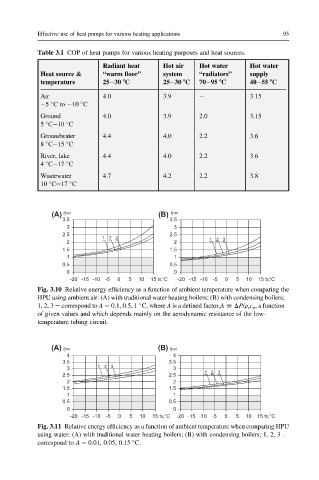
Effective use of heat pumps for various heating applications 95
Table 3.1 COP of heat pumps for various heating purposes and heat sources.
Radiant heat Hot air Hot water Hot water
Heat source & “warm floor” system “radiators” supply
temperature 25e30 8C 25e30 8C 70e95 8C 40e55 8C
Air 4.0 3.9 e 3.15
5 Cto 10 C
Ground 4.0 3.9 2.0 3.15
5 Ce10 C
Groundwater 4.4 4.0 2.2 3.6
8 Ce15 C
River, lake 4.4 4.0 2.2 3.6
4 Ce17 C
Wastewater 4.7 4.2 2.2 3.8
10 Ce17 C
(A) η rel (B) η rel
3.5 3.5
3 3
2.5 2.5
12 3 12 3
2 2
1.5 1.5
1 1
0.5 0.5
0 0
-20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 t0,°C -20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 t0,°C
Fig. 3.10 Relative energy efficiency as a function of ambient temperature when comparing the
HPU using ambient air: (A) with traditional water heating boilers; (B) with condensing boilers;
1, 2, 3 e correspond to A ¼ 0.1, 0.5, 1 C, where A is a defined factor,A h DP/r s c p , a function
of given values and which depends mainly on the aerodynamic resistance of the low-
temperature tubing circuit.
(A) η rel (B) η rel
4 4
3.5 3.5
3 12 3 3
2.5 2.5 1 2 3
2 2
1.5 1.5
1 1
0.5 0.5
0 0
-20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 t0,°C -20 -15 -10 -5 0 5 10 15 t0,°C
Fig. 3.11 Relative energy efficiency as a function of ambient temperature when comparing HPU
using water: (A) with traditional water heating boilers; (B) with condensing boilers; 1, 2, 3 -
correspond to A ¼ 0.01, 0.05, 0.15 C.