Page 68 - Low Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
P. 68
Characteristics of low-temperature energy sources for heat pumps 57
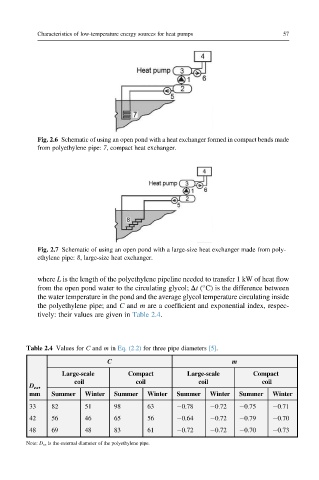
Fig. 2.6 Schematic of using an open pond with a heat exchanger formed in compact bends made
from polyethylene pipe: 7, compact heat exchanger.
Fig. 2.7 Schematic of using an open pond with a large-size heat exchanger made from poly-
ethylene pipe: 8, large-size heat exchanger.
where L is the length of the polyethylene pipeline needed to transfer 1 kW of heat flow
from the open pond water to the circulating glycol; Dt ( C) is the difference between
the water temperature in the pond and the average glycol temperature circulating inside
the polyethylene pipe; and C and m are a coefficient and exponential index, respec-
tively: their values are given in Table 2.4.
Table 2.4 Values for C and m in Eq. (2.2) for three pipe diameters [5].
C m
Large-scale Compact Large-scale Compact
coil coil coil coil
D ex ,
mm Summer Winter Summer Winter Summer Winter Summer Winter
33 82 51 98 63 0.78 0.72 0.75 0.71
42 56 46 65 56 0.64 0.72 0.79 0.70
48 69 48 83 61 0.72 0.72 0.70 0.73
Note: D ex is the external diameter of the polyethylene pipe.