Page 73 - Low Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
P. 73
62 Low-Temperature Energy Systems with Applications of Renewable Energy
2.4.3 Sewer drains
2.4.3.1 Sewer water
Sewer drains are considered to be an almost ideal source of low potential heat for heat
pumps. Utilization of such heat can be much more effective than the use of soil heat
due to constant high temperature of waste water during a heating period, high thermal
power, and good heat and physical characteristics. The direct use of sewer drain heat
by means of heat exchangers without their being located inside the flows or in vessels
of liquid drains is of practical interest.
The technical and economic efficiency of such a solution relating to heat pump heat
supply for city infrastructure loads was evaluated in Ref. [10]. High-efficiency com-
mercial heat pumps of water-water mode were used for the analyses. Two variants
were considered for locating heat exchangers to extract heat from sewer drains
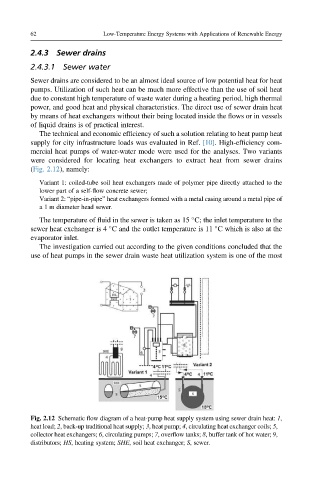
(Fig. 2.12), namely:
Variant 1: coiled-tube soil heat exchangers made of polymer pipe directly attached to the
lower part of a self-flow concrete sewer;
Variant 2: “pipe-in-pipe” heat exchangers formed with a metal casing around a metal pipe of
a 1 m diameter head sewer.
The temperature of fluid in the sewer is taken as 15 C; the inlet temperature to the
sewer heat exchanger is 4 C and the outlet temperature is 11 C which is also at the
evaporator inlet.
The investigation carried out according to the given conditions concluded that the
use of heat pumps in the sewer drain waste heat utilization system is one of the most
Fig. 2.12 Schematic flow diagram of a heat-pump heat supply system using sewer drain heat: 1,
heat load; 2, back-up traditional heat supply; 3,heatpump; 4, circulating heat exchanger coils; 5,
collector heat exchangers; 6, circulating pumps; 7,overflow tanks; 8, buffer tank of hot water; 9,
distributors; HS, heating system; SHE, soil heat exchanger; S,sewer.