Page 121 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 121
106 ——— MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
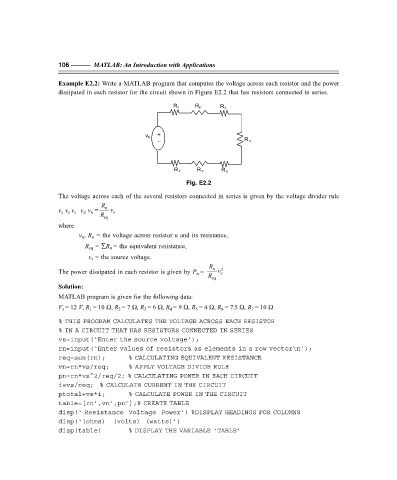
Example E2.2: Write a MATLAB program that computes the voltage across each resistor and the power
dissipated in each resistor for the circuit shown in Figure E2.2 that has resistors connected in series.
R 1 R 2 R 3
+
v S
– R 4
R 7 R 6 R 5
Fig. E2.2
The voltage across each of the several resistors connected in series is given by the voltage divider rule
R
v s v s v s v n v n = n v s
R eq
where
v n , R n = the voltage across resistor n and its resistance,
R eq = ∑R n = the equivalent resistance,
v s = the source voltage.
R
The power dissipated in each resistor is given by P n = n v 2 s
R eq
Solution:
MATLAB program is given for the following data:
V s = 12 V, R 1 = 10 Ω, R 2 = 7 Ω, R 3 = 6 Ω, R 4 = 9 Ω, R 5 = 4 Ω, R 6 = 7.5 Ω, R 7 = 10 Ω
% THIS PROGRAM CALCULATES THE VOLTAGE ACROSS EACH RESISTOR
% IN A CIRCUIT THAT HAS RESISTORS CONNECTED IN SERIES
vs=input(‘Enter the source voltage’);
rn=input(‘Enter values of resistors as elements in a row vector\n’);
req=sum(rn); % CALCULATING EQUIVALENT RESISTANCE
vn=rn*vs/req; % APPLY VOLTAGE DIVIDE RULE
pn=rn*vs^2/req/2; % CALCULATING POWER IN EACH CIRCUIT
i=vs/req; % CALCULATE CURRENT IN THE CIRCUIT
ptotal=vs*i; % CALCULATE POWER IN THE CIRCUIT
table=[rn’,vn’,pn’];% CREATE TABLE
disp(‘ Resistance Voltage Power’) %DISPLAY HEADINGS FOR COLUMNS
disp(‘(ohms) (volts) (watts)’)
disp(table) % DISPLAY THE VARIABLE ‘TABLE’
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09