Page 140 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 140
Control Systems ——— 125
G (s) transfer function of the controller
c
G (s) transfer function of the plant or process
p
H (s) transfer function of the sensor or output transducer = G (s)
s
R (s) reference input, transfer function of r(t).
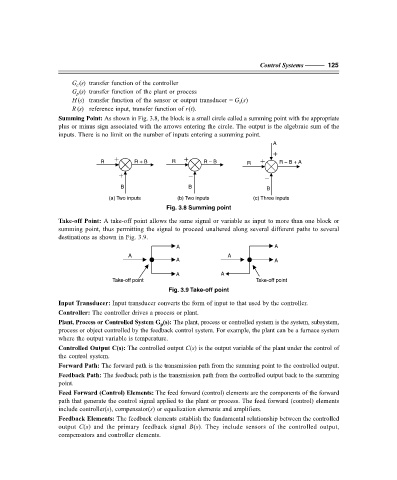
Summing Point: As shown in Fig. 3.8, the block is a small circle called a summing point with the appropriate
plus or minus sign associated with the arrows entering the circle. The output is the algebraic sum of the
inputs. There is no limit on the number of inputs entering a summing point.
A
+
R + R + B R + R – B R + R – B + A
+ – –
B B B
(a) Two inputs (b) Two inputs (c) Three inputs
Fig. 3.8 Summing point
Take-off Point: A take-off point allows the same signal or variable as input to more than one block or
summing point, thus permitting the signal to proceed unaltered along several different paths to several
destinations as shown in Fig. 3.9.
A A
A A
A A
A A
Take-off point Take-off point
Fig. 3.9 Take-off point
Input Transducer: Input transducer converts the form of input to that used by the controller.
Controller: The controller drives a process or plant.
Plant, Process or Controlled System G (s): The plant, process or controlled system is the system, subsystem,
p
process or object controlled by the feedback control system. For example, the plant can be a furnace system
where the output variable is temperature.
Controlled Output C(s): The controlled output C(s) is the output variable of the plant under the control of
the control system.
Forward Path: The forward path is the transmission path from the summing point to the controlled output.
Feedback Path: The feedback path is the transmission path from the controlled output back to the summing
point.
Feed Forward (Control) Elements: The feed forward (control) elements are the components of the forward
path that generate the control signal applied to the plant or process. The feed forward (control) elements
include controller(s), compensator(s) or equalization elements and amplifiers.
Feedback Elements: The feedback elements establish the fundamental relationship between the controlled
output C(s) and the primary feedback signal B(s). They include sensors of the controlled output,
compensators and controller elements.
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09