Page 168 - MEMS Mechanical Sensors
P. 168
7.3 Resonant and SAW Devices 157
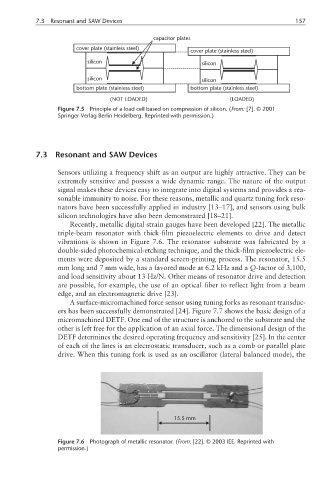
capacitor plates
cover plate (stainless steel)
cover plate (stainless steel)
silicon silicon
silicon silicon
bottom plate (stainless steel) bottom plate (stainless steel)
(NOT LOADED) (LOADED)
Figure 7.5 Principle of a load cell based on compression of silicon. (From: [7]. © 2001
Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg. Reprinted with permission.)
7.3 Resonant and SAW Devices
Sensors utilizing a frequency shift as an output are highly attractive. They can be
extremely sensitive and possess a wide dynamic range. The nature of the output
signal makes these devices easy to integrate into digital systems and provides a rea-
sonable immunity to noise. For these reasons, metallic and quartz tuning fork reso-
nators have been successfully applied in industry [13–17], and sensors using bulk
silicon technologies have also been demonstrated [18–21].
Recently, metallic digital strain gauges have been developed [22]. The metallic
triple-beam resonator with thick-film piezoelectric elements to drive and detect
vibrations is shown in Figure 7.6. The resonator substrate was fabricated by a
double-sided photochemical-etching technique, and the thick-film piezoelectric ele-
ments were deposited by a standard screen-printing process. The resonator, 15.5
mm long and 7 mm wide, has a favored mode at 6.2 kHz and a Q-factor of 3,100,
and load sensitivity about 13 Hz/N. Other means of resonator drive and detection
are possible, for example, the use of an optical fiber to reflect light from a beam
edge, and an electromagnetic drive [23].
A surface-micromachined force sensor using tuning forks as resonant transduc-
ers has been successfully demonstrated [24]. Figure 7.7 shows the basic design of a
micromachined DETF. One end of the structure is anchored to the substrate and the
other is left free for the application of an axial force. The dimensional design of the
DETF determines the desired operating frequency and sensitivity [25]. In the center
of each of the lines is an electrostatic transducer, such as a comb or parallel plate
drive. When this tuning fork is used as an oscillator (lateral balanced mode), the
15.5mmmm
15.5
Figure 7.6 Photograph of metallic resonator. (From: [22]. © 2003 IEE. Reprinted with
permission.)