Page 347 - MEMS and Microstructures in Aerospace Applications
P. 347
Osiander / MEMS and microstructures in Aerospace applications DK3181_c015 Final Proof page 340 1.9.2005 12:53pm
340 MEMS and Microstructures in Aerospace Applications
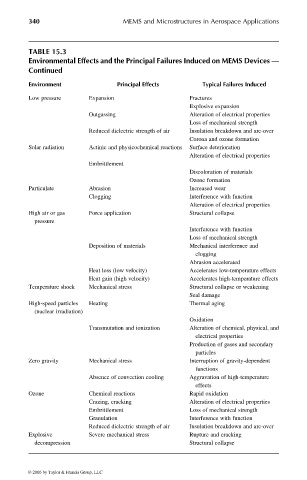
TABLE 15.3
Environmental Effects and the Principal Failures Induced on MEMS Devices —
Continued
Environment Principal Effects Typical Failures Induced
Low pressure Expansion Fractures
Explosive expansion
Outgassing Alteration of electrical properties
Loss of mechanical strength
Reduced dielectric strength of air Insulation breakdown and arc-over
Corona and ozone formation
Solar radiation Actinic and physicochemical reactions Surface deterioration
Alteration of electrical properties
Embrittlement
Discoloration of materials
Ozone formation
Particulate Abrasion Increased wear
Clogging Interference with function
Alteration of electrical properties
High air or gas Force application Structural collapse
pressure
Interference with function
Loss of mechanical strength
Deposition of materials Mechanical interference and
clogging
Abrasion accelerated
Heat loss (low velocity) Accelerates low-temperature effects
Heat gain (high velocity) Accelerates high-temperature effects
Temperature shock Mechanical stress Structural collapse or weakening
Seal damage
High-speed particles Heating Thermal aging
(nuclear irradiation)
Oxidation
Transmutation and ionization Alteration of chemical, physical, and
electrical properties
Production of gases and secondary
particles
Zero gravity Mechanical stress Interruption of gravity-dependent
functions
Absence of convection cooling Aggravation of high-temperature
effects
Ozone Chemical reactions Rapid oxidation
Crazing, cracking Alteration of electrical properties
Embrittlement Loss of mechanical strength
Granulation Interference with function
Reduced dielectric strength of air Insulation breakdown and arc-over
Explosive Severe mechanical stress Rupture and cracking
decompression Structural collapse
© 2006 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC