Page 109 - Macromolecular Crystallography
P. 109
98 MACROMOLECULAR CRYS TALLOGRAPHY
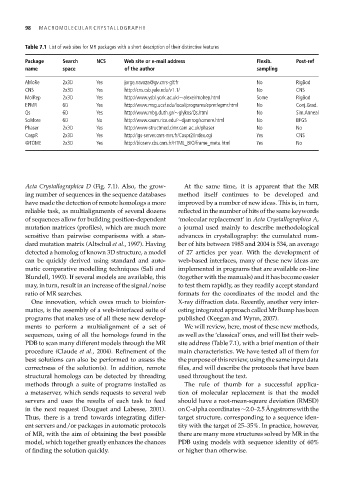
Table 7.1 List of web sites for MR packages with a short description of their distinctive features
Package Search NCS Web site or e-mail address Flexib. Post-ref
name space of the author sampling
AMoRe 2x3D Yes jorge.navaza@gv.cnrs-gif.fr No RigBod
CNS 2x3D Yes http://cns.csb.yale.edu/v1.1/ No CNS
MolRep 2x3D Yes http://www.ysbl.york.ac.uk/∼alexei/molrep.html Some RigBod
EPMR 6D Yes http://www.msg.ucsf.edu/local/programs/epmr/epmr.html No Conj.Grad.
Qs 6D Yes http://www.mbg.duth.gr/∼glykos/Qs.html No Sim.Anneal
SoMore 6D No http://www.caam.rice.edu/∼djamrog/somore.html No BFGS
Phaser 2x3D Yes http://www-structmed.cimr.cam.ac.uk/phaser No No
CaspR 2x3D Yes http://igs-server.cnrs-mrs.fr/Caspr2/index.cgi Yes CNS
@TOME 2x3D Yes http://bioserv.cbs.cnrs.fr/HTML_BIO/frame_meta.html Yes No
Acta Crystallographica D (Fig. 7.1). Also, the grow- At the same time, it is apparent that the MR
ing number of sequences in the sequence databases method itself continues to be developed and
have made the detection of remote homologs a more improved by a number of new ideas. This is, in turn,
reliable task, as multialignments of several dozens reflected in the number of hits of the same keywords
of sequences allow for building position-dependent ‘molecular replacement’ in Acta Crystallographica A,
mutation matrices (profiles), which are much more a journal used mainly to describe methodological
sensitive than pairwise comparisons with a stan- advances in crystallography: the cumulated num-
dard mutation matrix (Altschul et al., 1997). Having ber of hits between 1985 and 2004 is 534, an average
detected a homolog of known 3D structure, a model of 27 articles per year. With the development of
can be quickly derived using standard and auto- web-based interfaces, many of these new ideas are
matic comparative modelling techniques (Sali and implemented in programs that are available on-line
Blundell, 1993). If several models are available, this (together with the manuals) and it has become easier
may, in turn, result in an increase of the signal/noise to test them rapidly, as they readily accept standard
ratio of MR searches. formats for the coordinates of the model and the
One innovation, which owes much to bioinfor- X-ray diffraction data. Recently, another very inter-
matics, is the assembly of a web-interfaced suite of esting integrated approach called Mr Bump has been
programs that makes use of all these new develop- published (Keegan and Wynn, 2007).
ments to perform a multialignment of a set of We will review, here, most of these new methods,
sequences, using of all the homologs found in the as well as the ‘classical’ ones, and will list their web-
PDB to scan many different models through the MR site address (Table 7.1), with a brief mention of their
procedure (Claude et al., 2004). Refinement of the main characteristics. We have tested all of them for
best solutions can also be performed to assess the the purpose of this review, using the same input data
correctness of the solution(s). In addition, remote files, and will describe the protocols that have been
structural homologs can be detected by threading used throughout the text.
methods through a suite of programs installed as The rule of thumb for a successful applica-
a metaserver, which sends requests to several web tion of molecular replacement is that the model
servers and uses the results of each task to feed should have a root-mean-square deviation (RMSD)
in the next request (Douguet and Labesse, 2001). onC-alphacoordinates∼2.0–2.5 Ångstromswiththe
Thus, there is a trend towards integrating differ- target structure, corresponding to a sequence iden-
ent servers and/or packages in automatic protocols tity with the target of 25–35%. In practice, however,
of MR, with the aim of obtaining the best possible there are many more structures solved by MR in the
model, which together greatly enhances the chances PDB using models with sequence identity of 60%
of finding the solution quickly. or higher than otherwise.