Page 283 - Manufacturing Engineering and Technology - Kalpakjian, Serope : Schmid, Steven R.
P. 283
2 2 Chapter 11 Metal-Casting Processes and Equipment
ll.2 Expendable-mold, Permanent-pattern
Castmg Processes
The major categories of expendable-mold, permanent-pattern casting processes are
sand, shell mold, plaster mold, ceramic mold, and vacuum casting.
I l.2.I Sand Casting
The traditional method of casting metals is in sand molds and has been used for mil-
lennia. Sand casting is still the most prevalent form of casting; in the United States
alone, about 15 million tons of metal are cast by this method each year. Typical ap-
plications of sand casting include machine bases, large turbine impellers, propellers,
plumbing fixtures, and a wide variety of other products and components. The capa-
bilities of sand casting are given in Table 11.2.
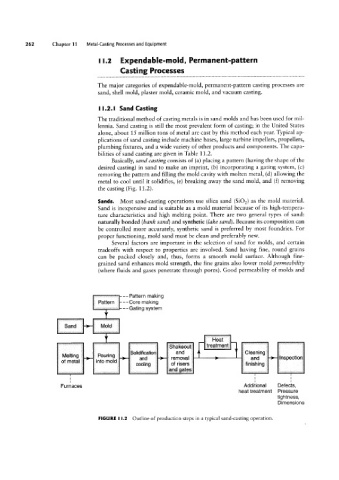
Basically, sand casting consists of (a) placing a pattern (having the shape of the
desired casting) in sand to make an imprint, (b) incorporating a gating system, (c)
removing the pattern and filling the mold cavity with molten metal, (d) allowing the
metal to cool until it solidifies, (e) breaking away the sand mold, and (f) removing
the casting (Fig. 11.2).
Sands. Most sand-casting operations use silica sand (SiO2) as the mold material.
Sand is inexpensive and is suitable as a mold material because of its high-tempera-
ture characteristics and high melting point. There are two general types of sand:
naturally bonded (bank sand) and synthetic (lake sand). Because its composition can
be controlled more accurately, synthetic sand is preferred by most foundries. For
proper functioning, mold sand must be clean and preferably new.
Several factors are important in the selection of sand for molds, and certain
tradeoffs with respect to properties are involved. Sand having fine, round grains
can be packed closely and, thus, forms a smooth mold surface. Although fine-
grained sand enhances mold strength, the fine grains also lower mold permeability
(where fluids and gases penetrate through pores). Good permeability of molds and
""'”'”"'F-- Pattern making
» --Grating system
Pattern y--- Core making
Shakeout {f€§ VD¢Uf
5 Solidification and Cieaning
xiféqgl .irl;?)u‘f:g?d; and removal and Qlnspectiori
cooling of risers finishing
Q
4
e.., .... .... ?E!¢l.9@l?§ Q
.,....,.. .,., ...... Q
Furnaces Additional Detects,
heat treatment Pressure
tightness,
Dimensions
FIGURE |.2 Outline of production steps in a typical sand-casting operation.
I