Page 507 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 507
Throat
Thermocouples
Section 19.2
D Wire filter Melt Extrusion 487
Barrel
Barrel
screen
thermocouple
heater/cooler
liner
Bleak”
Barrel fiff:;“‘;m:m:: Ame'
Channel Feed sectior1'(l\/lelt section lVlelt-pumping section Screw
Gear reducer
(3)
Pitchlj
box Barrel
if llr'r rrrrl Fright
‘=ee;;§f;2§2fEs€;¢e¢r_r§§Lé2§§2§~¢;¢;;;;;;;¢r.;;2;§;;¢¢,§;¢££¢¢ `,'~ ."§;>f¢s;e2;&r»,r if
Barrel
lb)
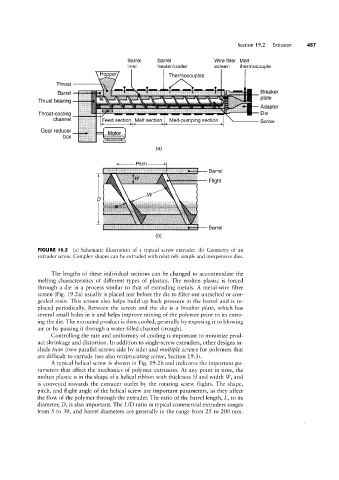
FIGURE I9.2 (a) Schematic illustration of a typical screw extruder. (b) Geometry of an
extruder screw. Complex shapes can be extruded with relatively simple and inexpensive dies.
The lengths of these individual sections can be changed to accommodate the
melting characteristics of different types of plastics. The molten plastic is forced
through a die in a process similar to that of extruding metals. A metal-wire filter
screen (Fig. 19.2a) usually is placed just before the die to filter out unmelted or con-
gealed resin. This screen also helps build up back pressure in the barrel and is re-
placed periodically. Between the screen and the die is a breaker plate, which has
several small holes in it and helps improve mixing of the polymer prior to its enter-
ing the die. The extruded product is then cooled, generally by exposing it to blowing
air or by passing it through a water-filled channel (trough).
Controlling the rate and uniformity of cooling is important to minimize prod-
uct shrinkage and distortion. In addition to single-screw extruders, other designs in-
clude twin (two parallel screws side by side) and multiple screws for polymers that
are difficult to extrude (see also reciprocating screw, Section 193).
A typical helical screw is shown in Fig. 19.2b and indicates the important pa-
rameters that affect the mechanics of polymer extrusion. At any point in time, the
molten plastic is in the shape of a helical ribbon with thickness H and width W, and
is conveyed towards the extruder outlet by the rotating screw flights. The shape,
pitch, and flight angle of the helical screw are important parameters, as they affect
the flow of the polymer through the extruder. The ratio of the barrel length, L, to its
diameter, D, is also important. The L/D ratio in typical commercial extruders ranges
from 5 to 30, and barrel diameters are generally in the range from 25 to 200 mm.