Page 523 - 04. Subyek Engineering Materials - Manufacturing, Engineering and Technology SI 6th Edition - Serope Kalpakjian, Stephen Schmid (2009)
P. 523
Section 19.7 Compression Molding 503
molds have small through-holes in order to aid vacuum forming. These holes typi-
cally are less than 0.5 mm in diameter; otherwise, they would leave marks on the
parts formed. Defects encountered in thermoforming include (a) tearing of the sheet
during forming, (bl nonuniform wall thickness, (c) improperly filled molds, (d) poor
part definition, and (e) lack of surface details.
l9.7 Compression Molding
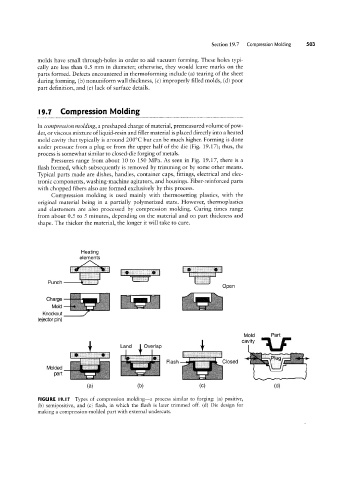
In compression molding, a preshaped charge of material, premeasured volume of pow-
der, or viscous mixture of liquid-resin and filler material is placed directly into a heated
mold cavity that typically is around 200°C but can be much higher. Forming is done
under pressure from a plug or from the upper half of the die (Fig. 19.17); thus, the
process is somewhat similar to closed-die forging of metals.
Pressures range from about 10 to 150 MPa. As seen in Fig. 19.17, there is a
flash formed, which subsequently is removed by trimming or by some other means.
Typical parts made are dishes, handles, container caps, fittings, electrical and elec-
tronic components, washing-machine agitators, and housings. Fiber-reinforced parts
with chopped fibers also are formed exclusively by this process.
Compression molding is used mainly with thermosetting plastics, with the
original material being in a partially polymerized state. However, thermoplastics
and elastomers are also processed by compression molding. Curing times range
from about 0.5 to 5 minutes, depending on the material and on part thickness and
shape. The thicker the material, the longer it will take to cure.
Heating
Q
elements ,,_,
Punch a»~aa ~fs,f»fff,»=.~1~ ~~=f»»»
Open
Land Overlap cavity Part
Knockout
(ejector pin)
Mold
Q
...., ,...._..,,,..,.....
"~» 1 Flash Closed
:;;f
part it MW ,,
(H) (D) (C) (Ol)
FIGURE l9.|7 Types of compression molding-a process similar to forging: (a) positive,
(b) semipositive, and (c) flash, in which the flash is later trimmed off. (d) Die design for
making a compression-molded part with external undercuts.