Page 604 - Marine Structural Design
P. 604
580 Part V Risk Assessment
I Problemdefinition 1
I
Task analysis
I
- Error identification
I
Representation
I
MI 1 Quantification
Qualitative
I
Impact assessment
I Owurnentation I
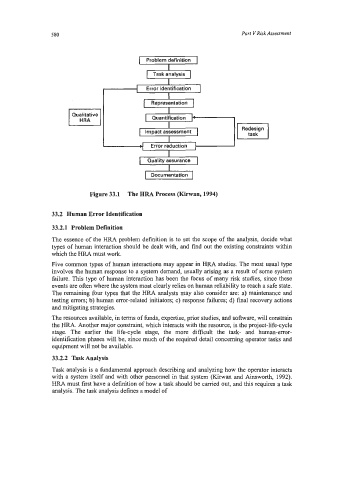
Figure 33.1 The HRA Process (Kiman, 1994)
33.2 Human Error Identification
33.2.1 Problem Definition
The essence of the HRA problem definition is to set the scope of the analysis, decide what
types of human interaction should be dealt with, and find out the existing constraints within
which the HRA must work.
Five common types of human interactions may appear in HRA studies. The most usual type
involves the human response to a system demand, usually arising as a result of some system
failure. This type of human interaction has been the focus of many risk studies, since these
events are often where the system most clearly relies on human reliability to reach a safe state.
The remaining four types that the HRA analysts may also consider are: a) maintenance and
testing errors; b) human error-related initiators; c) response failures; d) final recovery actions
and mitigating strategies.
The resources available, in terms of funds, expertise, prior studies, and sohare, will constrain
the HRA. Another major constraint, which interacts with the resource, is the project-life-cycle
stage. The earlier the life-cycle stage, the more difficult the task- and human-mr-
identification phases will be, since much of the required detail concerning operator tasks and
equipment will not be available.
33.2.2 Task Analysis
Task analysis is a fhdamental approach describing and analyzing how the operator interacts
with a system itself and with other personnel in that system (Kinvan and Ainsworth, 1992).
HRA must first have a definition of how a task should be carried out, and this requires a task
analysis. The task analysis defines a model of