Page 315 - Marks Calculation for Machine Design
P. 315
P1: Shashi
January 4, 2005
Brown˙C07
Brown.cls
Step 11. Calculate the area moment of inertia (I) for the rectangular cross section as
1 3 1 15:4 FATIGUE AND DYNAMIC DESIGN −4 4 −12 4 297
3
I = bh = (1.25 cm)(0.16 cm) = 4.27 × 10 cm = 4.27 × 10 m
12 12
Step 12. Calculate the mean bending stress (σ m ) and the alternating bending stress (σ a ) as
M m c (1.08 N · m)(0.0008 m)
σ m = = = 202.3MPa
I 4.27 × 10 −12 m 4
M a c (0.43 N · m)(0.0008 m)
σ a = = = 80.6MPa
I 4.27 × 10 −12 m 4
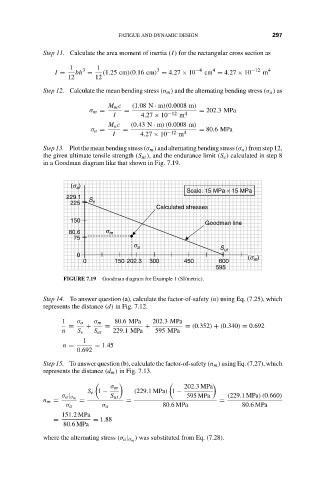
Step13. Plotthemeanbendingstress (σ m )andalternatingbendingstress(σ a )fromstep12,
the given ultimate tensile strength (S ut ), and the endurance limit (S e ) calculated in step 8
in a Goodman diagram like that shown in Fig. 7.19.
(s )
a
Scale: 15 MPa × 15 MPa
229.1 S
225 e
Calculated stresses
150 Goodman line
80.6 s m
75
s a S ut
0
(s m )
0 150 202.3 300 450 600
595
FIGURE 7.19 Goodman diagram for Example 1 (SI/metric).
Step 14. To answer question (a), calculate the factor-of-safety (n) using Eq. (7.25), which
represents the distance (d) in Fig. 7.12.
1 σ a σ m 80.6MPa 202.3MPa
= + = + = (0.352) + (0.340) = 0.692
n S e S ut 229.1MPa 595 MPa
1
n = = 1.45
0.692
Step 15. To answer question (b), calculate the factor-of-safety (n m ) using Eq. (7.27), which
represents the distance (d m ) in Fig. 7.13.
σ m 202.3MPa
S e 1 − (229.1MPa) 1 −
σ a | σ m S ut 595 MPa (229.1MPa)(0.660)
n m = = = =
σ a σ a 80.6MPa 80.6MPa
151.2MPa
= = 1.88
80.6MPa
) was substituted from Eq. (7.28).
where the alternating stress (σ a | σ m