Page 61 - Marks Calculation for Machine Design
P. 61
P1: Sanjay
January 4, 2005
Brown˙C02
Brown.cls
V
Fb/L 16:18 BEAMS 43
+ b
0 x
a L
–
–Fa/L
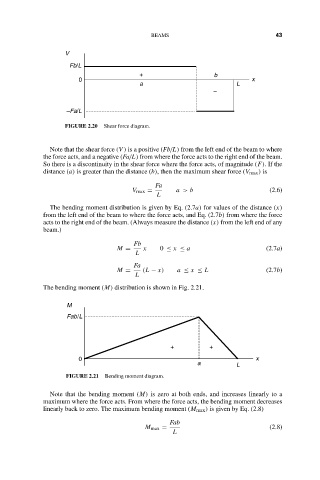
FIGURE 2.20 Shear force diagram.
Note that the shear force (V ) is a positive (Fb/L) from the left end of the beam to where
the force acts, and a negative (Fa/L) from where the force acts to the right end of the beam.
So there is a discontinuity in the shear force where the force acts, of magnitude (F).Ifthe
distance (a) is greater than the distance (b), then the maximum shear force (V max ) is
Fa
V max = a > b (2.6)
L
The bending moment distribution is given by Eq. (2.7a) for values of the distance (x)
from the left end of the beam to where the force acts, and Eq. (2.7b) from where the force
acts to the right end of the beam. (Always measure the distance (x) from the left end of any
beam.)
Fb
M = x 0 ≤ x ≤ a (2.7a)
L
Fa
M = (L − x) a ≤ x ≤ L (2.7b)
L
The bending moment (M) distribution is shown in Fig. 2.21.
M
Fab/L
+ +
0 x
a L
FIGURE 2.21 Bending moment diagram.
Note that the bending moment (M) is zero at both ends, and increases linearly to a
maximum where the force acts. From where the force acts, the bending moment decreases
linearly back to zero. The maximum bending moment (M max ) is given by Eq. (2.8)
Fab
M max = (2.8)
L