Page 192 - Materials Science and Engineering An Introduction
P. 192
164 • Chapter 5 / Diffusion
tion of 56.5 wt% Ni a distance of 15
m into the 5.25 The preexponential and activation energy for
4
Ni-Cu alloy referenced to the original interface. the diffusion of chromium in nickel are 1.1 10
2
Values for the preexponential and activation en- m /s and 272,000 J/mol, respectively. At what tem-
2
4
ergy for this diffusion system are 2.3 10 m /s perature will the diffusion coefficient have a value
2
and 252,000 J/mol. of 1.2 10 14 m /s?
5.17 Consider a diffusion couple composed of two 5.26 The activation energy for the diffusion of copper
cobalt-iron alloys; one has a composition of 75 wt% in silver is 193,000 J/mol. Calculate the diffusion
Co-25 wt% Fe; the other alloy composition is coefficient at 1200 K (927 C), given that D at
50 wt% Co-50 wt% Fe. If this couple is heated 1000 K (727 C) is 1.0 10 14 m /s.
2
to a temperature of 800 C (1073 K) for 20,000 s, The diffusion coefficients for nickel in iron are
determine how far from the original interface into 5.27 given at two temperatures, as follows:
the 50 wt% Co-50 wt% Fe alloy the composition
has increased to 52 wt% Co-48 wt% Fe. For the 2
6
diffusion coefficient, assume values of 6.6 10 T(K) D(m /s)
2
m /s and 247,000 J/mol, respectively, for the pre- 1473 2.2 10 15
exponential and activation energy. 1673 4.8 10 14
5.18 Consider a diffusion couple between silver and a (a) Determine the values of D 0 and the activation
gold alloy that contains 10 wt% silver. This couple energy Q d .
is heat treated at an elevated temperature and it
was found that after 850 s, the concentration of (b) What is the magnitude of D at 1300 C (1573 K)?
silver had increased to 12 wt% at 10
m from the 5.28 The diffusion coefficients for carbon in nickel are
interface into the Ag–Au alloy. Assuming preexpo- given at two temperatures, as follows:
6
nential and activation energy values of 7.2 10
2
m /s and 168,000 J/mol, respectively, compute the 2
temperature of this heat treatment. (Note: You may T( C) D(m /s)
find Figure 5.13 and Equation 5.15 helpful.) 600 5.5 10 14
5.19 For a steel alloy, it has been determined that a 700 3.9 10 13
carburizing heat treatment of 15 h duration will (a) Determine the values of D 0 and Q d .
raise the carbon concentration to 0.35 wt% at a
point 2.0 mm from the surface. Estimate the time (b) What is the magnitude of D at 850 C?
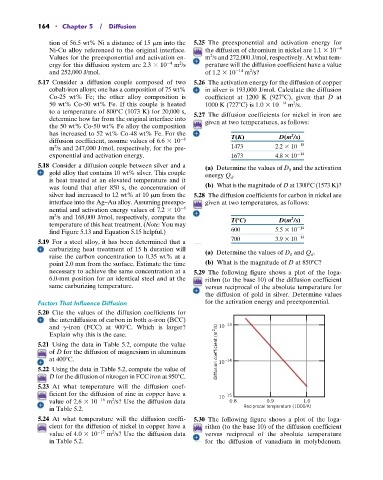
necessary to achieve the same concentration at a 5.29 The following figure shows a plot of the loga-
6.0-mm position for an identical steel and at the rithm (to the base 10) of the diffusion coefficient
same carburizing temperature. versus reciprocal of the absolute temperature for
the diffusion of gold in silver. Determine values
Factors That Influence Diffusion for the activation energy and preexponential.
5.20 Cite the values of the diffusion coefficients for
the interdiffusion of carbon in both a-iron (BCC)
and g-iron (FCC) at 900 C. Which is larger? 10 –13
Explain why this is the case.
5.21 Using the data in Table 5.2, compute the value
of D for the diffusion of magnesium in aluminum Diffusion coefficient (m 2 /s)
at 400 C. 10 –14
5.22 Using the data in Table 5.2, compute the value of
D for the diffusion of nitrogen in FCC iron at 950 C.
5.23 At what temperature will the diffusion coef-
ficient for the diffusion of zinc in copper have a 10 –15
2
value of 2.6 10 16 m /s? Use the diffusion data 0.8 0.9 1.0
in Table 5.2. Reciprocal temperature (1000/K)
5.24 At what temperature will the diffusion coeffi- 5.30 The following figure shows a plot of the loga-
cient for the diffusion of nickel in copper have a rithm (to the base 10) of the diffusion coefficient
2
value of 4.0 10 17 m /s? Use the diffusion data versus reciprocal of the absolute temperature
in Table 5.2. for the diffusion of vanadium in molybdenum.